Therapeutic modulation of eIF2α phosphorylation rescues TDP-43 toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease models
- PMID: 24336168
- PMCID: PMC3934366
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2853
Therapeutic modulation of eIF2α phosphorylation rescues TDP-43 toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease models
Abstract
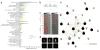
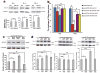
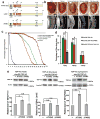
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal, late-onset neurodegenerative disease primarily affecting motor neurons. A unifying feature of many proteins associated with ALS, including TDP-43 and ataxin-2, is that they localize to stress granules. Unexpectedly, we found that genes that modulate stress granules are strong modifiers of TDP-43 toxicity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila melanogaster. eIF2α phosphorylation is upregulated by TDP-43 toxicity in flies, and TDP-43 interacts with a central stress granule component, polyA-binding protein (PABP). In human ALS spinal cord neurons, PABP accumulates abnormally, suggesting that prolonged stress granule dysfunction may contribute to pathogenesis. We investigated the efficacy of a small molecule inhibitor of eIF2α phosphorylation in ALS models. Treatment with this inhibitor mitigated TDP-43 toxicity in flies and mammalian neurons. These findings indicate that the dysfunction induced by prolonged stress granule formation might contribute directly to ALS and that compounds that mitigate this process may represent a novel therapeutic approach.
Figures

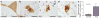

References
-
- Boillee S, Vande Velde C, Cleveland DW. ALS: a disease of motor neurons and their nonneuronal neighbors. Neuron. 2006;52:39–59. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland DW, Rothstein JD. From Charcot to Lou Gehrig: deciphering selective motor neuron death in ALS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:806–19. - PubMed
-
- Al-Chalabi A, et al. The genetics and neuropathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;124:339–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG10124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039074/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS053488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG17586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS53488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2OD004417/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073660/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS073660/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG032953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD004417/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AG32953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

