Serotonin contracts the rat mesenteric artery by inhibiting 4-aminopyridine-sensitive Kv channels via the 5-HT2A receptor and Src tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 24336234
- PMCID: PMC3880459
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2013.116
Serotonin contracts the rat mesenteric artery by inhibiting 4-aminopyridine-sensitive Kv channels via the 5-HT2A receptor and Src tyrosine kinase
Abstract
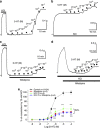
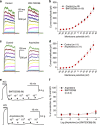
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)) is a neurotransmitter that regulates a variety of functions in the nervous, gastrointestinal and cardiovascular systems. Despite such importance, 5-HT signaling pathways are not entirely clear. We demonstrated previously that 4-aminopyridine (4-AP)-sensitive voltage-gated K(+) (Kv) channels determine the resting membrane potential of arterial smooth muscle cells and that the Kv channels are inhibited by 5-HT, which depolarizes the membranes. Therefore, we hypothesized that 5-HT contracts arteries by inhibiting Kv channels. Here we studied 5-HT signaling and the detailed role of Kv currents in rat mesenteric arteries using patch-clamp and isometric tension measurements. Our data showed that inhibiting 4-AP-sensitive Kv channels contracted arterial rings, whereas inhibiting Ca(2+)-activated K(+), inward rectifier K(+) and ATP-sensitive K(+) channels had little effect on arterial contraction, indicating a central role of Kv channels in the regulation of resting arterial tone. 5-HT-induced arterial contraction decreased significantly in the presence of high KCl or the voltage-gated Ca(2+) channel (VGCC) inhibitor nifedipine, indicating that membrane depolarization and the consequent activation of VGCCs mediate the 5-HT-induced vasoconstriction. The effects of 5-HT on Kv currents and arterial contraction were markedly prevented by the 5-HT2A receptor antagonists ketanserin and spiperone. Consistently, α-methyl 5-HT, a 5-HT2 receptor agonist, mimicked the 5-HT action on Kv channels. Pretreatment with a Src tyrosine kinase inhibitor, 4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine, prevented both the 5-HT-mediated vasoconstriction and Kv current inhibition. Our data suggest that 4-AP-sensitive Kv channels are the primary regulator of the resting tone in rat mesenteric arteries. 5-HT constricts the arteries by inhibiting Kv channels via the 5-HT2A receptor and Src tyrosine kinase pathway.
Figures




References
-
- Watts SW. 5-HT in systemic hypertension: foe, friend or fantasy. Clin Sci (Lond) 2005;108:399–412. - PubMed
-
- Miner LA, Backstrom JR, Sanders-Bush E, Sesack SR. Ultrastructural localization of serotonin2A receptors in the middle layers of the rat prelimbic prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience. 2003;116:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Roth BL, Hanizavareh SM, Blum AE. Serotonin receptors represent highly favorable molecular targets for cognitive enhancement in schizophrenia and other disorders. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004;174:17–24. - PubMed
-
- Berg KA, Harvey JA, Spampinato U, Clarke WP. Physiological and therapeutic relevance of constitutive activity of 5-HT 2A and 5-HT 2C receptors for the treatment of depression. Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:287–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
