Physical exercise habits correlate with gray matter volume of the hippocampus in healthy adult humans
- PMID: 24336512
- PMCID: PMC3860009
- DOI: 10.1038/srep03457
Physical exercise habits correlate with gray matter volume of the hippocampus in healthy adult humans
Abstract
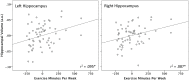
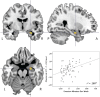
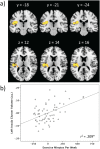
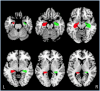
Physical activity facilitates neurogenesis of dentate cells in the rodent hippocampus, a brain region critical for memory formation and spatial representation. Recent findings in humans also suggest that aerobic exercise can lead to increased hippocampal volume and enhanced cognitive functioning in children and elderly adults. However, the association between physical activity and hippocampal volume during the period from early adulthood through middle age has not been effectively explored. Here, we correlated the number of minutes of self-reported exercise per week with gray matter volume of the hippocampus using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) in 61 healthy adults ranging from 18 to 45 years of age. After controlling for age, gender, and total brain volume, total minutes of weekly exercise correlated significantly with volume of the right hippocampus. Findings highlight the relationship between regular physical exercise and brain structure during early to middle adulthood.
Figures
References
-
- Wong R. O. & Ghosh A. Activity-dependent regulation of dendritic growth and patterning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 803–812; 10.1038/nrn941 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Cory S. The developing synapse: construction and modulation of synaptic structures and circuits. Science 298, 770–776; 10.1126/science.1075510 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Hua J. Y. & Smith S. J. Neural activity and the dynamics of central nervous system development. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 327–332; 10.1038/nn1218 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Casey B. J., Tottenham N., Liston C. & Durston S. Imaging the developing brain: what have we learned about cognitive development? Trends Cogn Sci 9, 104–110; 10.1016/j.tics.2005.01.011 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

