Extinction of remotely acquired fear depends on an inhibitory NR2B/PKA pathway in the retrosplenial cortex
- PMID: 24336715
- PMCID: PMC3858621
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3338-13.2013
Extinction of remotely acquired fear depends on an inhibitory NR2B/PKA pathway in the retrosplenial cortex
Abstract
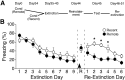
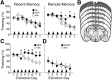
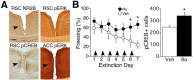
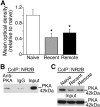
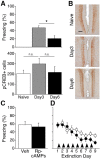
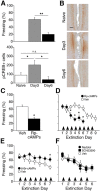
As memories age, their processing increasingly relies upon cortical rather than hippocampal circuits, but the adaptive significance and mechanisms of this shift are not fully understood. Here we investigated the behavioral features and cortical mechanisms underlying extinction of remotely versus recently acquired context fear in mice. Behaviorally, extinction and reinstatement were similar, but re-extinction of remote fear was significantly faster, suggesting time-dependent engagement of mechanisms specific for processing remote memory. Using pharmacological manipulations of NMDA receptors and associated signaling pathways in the in the retrosplenial cortex, we demonstrated that extinction of remote fear uniquely required NR2B-mediated downregulation of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)/cAMP response element-binding protein pathway. Interestingly, NR2B/PKA interactions weakened independently of the age of the memory, but the functional significance of this molecular change was evident only as memory retrieval became PKA-dependent over time. Thus, cortical PKA signaling may provide a molecular signature of when a memory has become "remote," and inhibition of this pathway may open the door for modulation of remote memories.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of fear extinction versus other affective behaviors by discrete cortical scaffolding complexes associated with NR2B and PKA signaling.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 13;5(10):e657. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.150. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26460481 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NMDA glutamate receptors, PKA, MAPK, and CAMKII in the hippocampus in extinction of conditioned fear.Hippocampus. 2003;13(1):53-8. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10043. Hippocampus. 2003. PMID: 12625457
-
Inhibition of PKA anchoring to A-kinase anchoring proteins impairs consolidation and facilitates extinction of contextual fear memories.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008 Jul;90(1):223-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2008.03.008. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2008. PMID: 18442935
-
N-Methyl D-aspartate receptor subunit signaling in fear extinction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):239-250. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5022-5. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30238131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurochemical and molecular mechanisms underlying the retrieval-extinction effect.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):111-132. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5121-3. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30656364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retrosplenial Cortex and Long-Term Memory: Molecules to Behavior.Neural Plast. 2015;2015:414173. doi: 10.1155/2015/414173. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Neural Plast. 2015. PMID: 26380115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-induced generalization of negative memories is mediated by an extended hippocampal circuit.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Jan;47(2):516-523. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01174-4. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 34493828 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin A Differentially Influences the Extinction Retention of Recent and Remote Fear Memory.Front Neurosci. 2018 May 3;12:295. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00295. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29773974 Free PMC article.
-
The cannabinoid system in the retrosplenial cortex modulates fear memory consolidation, reconsolidation, and extinction.Learn Mem. 2015 Nov 16;22(12):584-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.039891.115. Print 2015 Dec. Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 26572648 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of fear extinction versus other affective behaviors by discrete cortical scaffolding complexes associated with NR2B and PKA signaling.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 13;5(10):e657. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.150. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26460481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao H, Ren WH, Zhu MY, Zhao ZQ, Zhang YQ. Activation of glycine site and GluN2B subunit of NMDA receptors is necessary for ERK/CREB signaling cascade in rostral anterior cingulated cortex in rats: implications for affective pain. Neurosci Bull. 2012;28:77–87. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1060-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
