Cryptic variation in morphological evolution: HSP90 as a capacitor for loss of eyes in cavefish
- PMID: 24337296
- PMCID: PMC4004346
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1240276
Cryptic variation in morphological evolution: HSP90 as a capacitor for loss of eyes in cavefish
Abstract
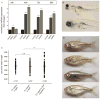
In the process of morphological evolution, the extent to which cryptic, preexisting variation provides a substrate for natural selection has been controversial. We provide evidence that heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) phenotypically masks standing eye-size variation in surface populations of the cavefish Astyanax mexicanus. This variation is exposed by HSP90 inhibition and can be selected for, ultimately yielding a reduced-eye phenotype even in the presence of full HSP90 activity. Raising surface fish under conditions found in caves taxes the HSP90 system, unmasking the same phenotypic variation as does direct inhibition of HSP90. These results suggest that cryptic variation played a role in the evolution of eye loss in cavefish and provide the first evidence for HSP90 as a capacitor for morphological evolution in a natural setting.
Figures


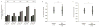
Comment in
-
Evolution. Cavefish study supports controversial evolutionary mechanism.Science. 2013 Dec 13;342(6164):1304. doi: 10.1126/science.342.6164.1304. Science. 2013. PMID: 24337270 No abstract available.
-
Evolution: An eye for cryptic variation.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Feb;15(2):64. doi: 10.1038/nrg3660. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24366183 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

