A novel compound heterozygous mutation in the GJB2 gene causing non-syndromic hearing loss in a family
- PMID: 24337325
- PMCID: PMC3896467
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1581
A novel compound heterozygous mutation in the GJB2 gene causing non-syndromic hearing loss in a family
Abstract
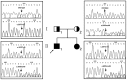
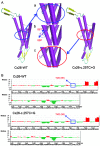
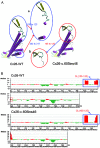
Mutations in the GJB2 gene are responsible for up to 50% of cases of non-syndromic recessive hearing loss, with c.35delG, c.167delT and c.235delC being the predominant mutations in many world populations. However, a large number of rare mutations in this gene may also contribute to hearing loss. The aim of the present study was to conduct a clinical and molecular characterization of a Chinese family with non-syndromic hearing loss. Sequence analysis of the GJB2 gene led to the identification of a novel compound heterozygous mutation c.257C>G (p.T86R)/c.605ins46 in two profoundly deaf siblings whose hearing parents were each heterozygous, either for the c.257C>G (paternal) or for the c.605ins46 (maternal) mutations. Both c.257C>G and c.605ins46 are rare GJB2 mutations that have previously been reported to segregate with autosomal recessive hearing loss exclusively in East Asian populations. To study the pathogenic effect of the compound heterozygous mutation, a three-dimensional model was constructed and Anolea mean force potential energy was predicted for a bioinformatic structural analysis. HEK293 cells were used to study the pathogenic effect of mutant connexin 26 proteins. The results suggested that the c.257C>G (p.T86R)/c.605ins46 mutations in the GJB2 gene provides a novel molecular explanation for the role of the GJB2 gene in hearing loss.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel GJB2 compound heterozygous mutation c.257C>G (p.T86R)/c.176del16 (p.G59A fs*18) causes sensorineural hearing loss in a Chinese family.J Clin Lab Anal. 2018 Sep;32(7):e22444. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22444. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018. PMID: 29665173 Free PMC article.
-
GJB2 Mutation Spectrum and Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in 1067 Han Chinese Subjects with Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 4;10(6):e0128691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128691. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26043044 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin 26 (GJB2) gene mutations linked with autosomal recessive non-syndromic sensor neural hearing loss in the Iraqi population.J Med Life. 2021 Nov-Dec;14(6):841-846. doi: 10.25122/jml-2021-0152. J Med Life. 2021. PMID: 35126756 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate hearing loss and pseudodominant inheritance due to L90P/35delG mutations in the GJB2 (connexin 26) gene.Genet Couns. 2003;14(4):379-86. Genet Couns. 2003. PMID: 14738110 Review.
-
Compound heterozygosity for dominant and recessive GJB2 mutations in a Tunisian family and association with successful cochlear implant outcome.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Sep;77(9):1481-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23856378 Review.
Cited by
-
Polymorphism of the 86th amino acid in CX26 protein and hereditary deafness.J Otol. 2016 Jun;11(2):84-87. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Otol. 2016. PMID: 29937815 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Consequences of Pathogenic Variants of the GJB2 Gene (Cx26) Localized in Different Cx26 Domains.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 13;13(10):1521. doi: 10.3390/biom13101521. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel GJB2 compound heterozygous mutation c.257C>G (p.T86R)/c.176del16 (p.G59A fs*18) causes sensorineural hearing loss in a Chinese family.J Clin Lab Anal. 2018 Sep;32(7):e22444. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22444. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018. PMID: 29665173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morton CC. Genetics, genomics and gene discovery in the auditory system. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1229–1240. - PubMed
-
- Kenneson A, Van Naarden Braun K, Boyle C. GJB2 (connexin 26) variants and nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss: a HuGE review. Genet Med. 2002;4:258–274. - PubMed
-
- Estivill X, Fortina P, Surrey S, et al. Connexin-26 mutations in sporadic and inherited sensorineural deafness. Lancet. 1998;351:394–398. - PubMed
-
- Morell RJ, Kim HJ, Hood LJ, et al. Mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) among Ashkenazi Jews with nonsyndromic recessive deafness. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1500–1505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

