Development of ICF Core Sets to standardize assessment of functioning and impairment in ADHD: the path ahead
- PMID: 24337412
- PMCID: PMC4246121
- DOI: 10.1007/s00787-013-0496-5
Development of ICF Core Sets to standardize assessment of functioning and impairment in ADHD: the path ahead
Abstract
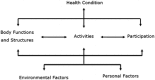
In the study of health and quality of life in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), it is of paramount importance to include assessment of functioning. The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) provides a comprehensive, universally accepted framework for the description of functioning in relation to health conditions. In this paper, the authors outline the process to develop ICF Core Sets for ADHD. ICF Core Sets are subgroups of ICF categories selected to capture the aspects of functioning that are most likely to be affected in specific disorders. The ICF categories that will be included in the ICF Core Sets for ADHD will be determined at an ICF Core Set Consensus Conference, wherein evidence from four preliminary studies (a systematic review, an expert survey, a patient and caregiver qualitative study, and a clinical cross-sectional study) will be integrated. Comprehensive and Brief ICF Core Sets for ADHD will be developed with the goal of providing useful standards for research and clinical practice, and to generate a common language for the description of functioning in ADHD in different areas of life and across the lifespan.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (1992-1994) International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, tenth revision. In: World Health Organization, vol 1–3. Geneva, Switzerland - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

