Insig proteins mediate feedback inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in the intestine
- PMID: 24337570
- PMCID: PMC3900961
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.524041
Insig proteins mediate feedback inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in the intestine
Abstract
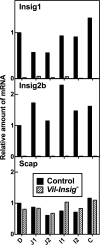
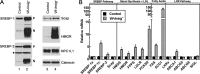
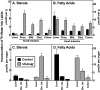
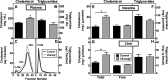
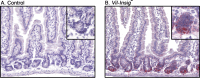
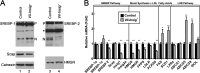
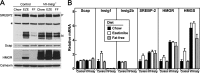
Enterocytes are the only cell type that must balance the de novo synthesis and absorption of cholesterol, although the coordinate regulation of these processes is not well understood. Our previous studies demonstrated that enterocytes respond to the pharmacological blockade of cholesterol absorption by ramping up de novo sterol synthesis through activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 (SREBP-2). Here, we genetically disrupt both Insig1 and Insig2 in the intestine, two closely related proteins that are required for the feedback inhibition of SREBP and HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR). This double knock-out was achieved by generating mice with an intestine-specific deletion of Insig1 using Villin-Cre in combination with a germ line deletion of Insig2. Deficiency of both Insigs in enterocytes resulted in constitutive activation of SREBP and HMGR, leading to an 11-fold increase in sterol synthesis in the small intestine and producing lipidosis of the intestinal crypts. The intestine-derived cholesterol accumulated in plasma and liver, leading to secondary feedback inhibition of hepatic SREBP2 activity. Pharmacological blockade of cholesterol absorption was unable to further induce the already elevated activities of SREBP-2 or HMGR in Insig-deficient enterocytes. These studies confirm the essential role of Insig proteins in the sterol homeostasis of enterocytes.
Keywords: Cholesterol Regulation; Dyslipidemia; Ezetimibe; Gene Knockout; HMG-CoA Reductase; Insig; Intestine; Lipid Absorption; Lipid Synthesis; SREBP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scavenger receptor CD36 mediates inhibition of cholesterol synthesis via activation of the PPARγ/PGC-1α pathway and Insig1/2 expression in hepatocytes.FASEB J. 2014 Apr;28(4):1910-23. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-240168. Epub 2013 Dec 26. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24371122
-
Blockade of cholesterol absorption by ezetimibe reveals a complex homeostatic network in enterocytes.J Lipid Res. 2012 Jul;53(7):1359-68. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M027599. Epub 2012 Apr 22. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22523394 Free PMC article.
-
Schoenheimer effect explained--feedback regulation of cholesterol synthesis in mice mediated by Insig proteins.J Clin Invest. 2005 Sep;115(9):2489-98. doi: 10.1172/JCI25614. Epub 2005 Aug 11. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16100574 Free PMC article.
-
Dual functions of Insig proteins in cholesterol homeostasis.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Dec 18;11:173. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-173. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 23249523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-induced gene: a new regulator in lipid metabolism.Peptides. 2010 Nov;31(11):2145-50. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.07.020. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 20817058 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Accelerated Degradation to Feedback Regulation of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase and Cholesterol Metabolism in the Liver.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 24;291(26):13479-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.728469. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129778 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol auxotrophy and intolerance to ezetimibe in mice with SREBP-2 deficiency in the intestine.J Lipid Res. 2017 Oct;58(10):1988-1998. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M077610. Epub 2017 Jun 19. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28630260 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pi, Glutamine and the Essential Amino Acids in Modulating the Metabolism in Diabetes and Cancer.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Aug 19;19(2):1731-1775. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00566-5. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 33520860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 1 polyisoprenoid diphosphate phosphatase modulates geranylgeranyl-mediated control of HMG CoA reductase and UBIAD1.Elife. 2021 Nov 29;10:e64688. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64688. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34842525 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental and extrahepatic physiological functions of SREBP pathway genes in mice.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Sep;81:98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 28736205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang T., Espenshade P. J., Wright M. E., Yabe D., Gong Y., Aebersold R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. (2002) Crucial step in cholesterol homeostasis. Sterols promote binding of SCAP to INSIG-1, a membrane protein that facilitates retention of SREBPs in ER. Cell 110, 489–500 - PubMed
-
- Sever N., Yang T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., DeBose-Boyd R. A. (2003) Accelerated degradation of HMG CoA reductase mediated by binding of insig-1 to its sterol-sensing domain. Mol. Cell 11, 25–33 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

