Tumor necrosis factor and transforming growth factor β regulate clock genes by controlling the expression of the cold inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRBP)
- PMID: 24337574
- PMCID: PMC3908406
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508200
Tumor necrosis factor and transforming growth factor β regulate clock genes by controlling the expression of the cold inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRBP)
Abstract
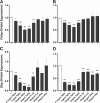
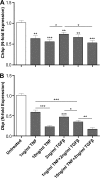
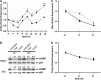
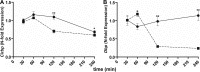
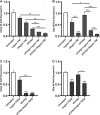
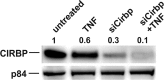
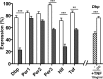
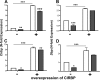
The circadian clock drives the rhythmic expression of a broad array of genes that orchestrate metabolism, sleep wake behavior, and the immune response. Clock genes are transcriptional regulators engaged in the generation of circadian rhythms. The cold inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRBP) guarantees high amplitude expression of clock. The cytokines TNF and TGFβ impair the expression of clock genes, namely the period genes and the proline- and acidic amino acid-rich basic leucine zipper (PAR-bZip) clock-controlled genes. Here, we show that TNF and TGFβ impair the expression of Cirbp in fibroblasts and neuronal cells. IL-1β, IL-6, IFNα, and IFNγ do not exert such effects. Depletion of Cirbp is found to increase the susceptibility of cells to the TNF-mediated inhibition of high amplitude expression of clock genes and modulates the TNF-induced cytokine response. Our findings reveal a new mechanism of cytokine-regulated expression of clock genes.
Keywords: Circadian Rhythms; Cytokine; Gene Expression; Innate Immunity; Metabolism; Sickness Behavior; Sleep.
Figures

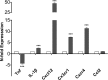
References
-
- Franken P., Dijk D. J. (2009) Circadian clock genes and sleep homeostasis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 29, 1820–1829 - PubMed
-
- Dibner C., Schibler U., Albrecht U. (2010) The mammalian circadian timing system: organization and coordination of central and peripheral clocks. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72, 517–549 - PubMed
-
- Ko C. H., Takahashi J. S. (2006) Molecular components of the mammalian circadian clock. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, R271–R277 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

