Chorismate pyruvate-lyase and 4-hydroxy-3-solanesylbenzoate decarboxylase are required for plastoquinone biosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803
- PMID: 24337576
- PMCID: PMC3908401
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511709
Chorismate pyruvate-lyase and 4-hydroxy-3-solanesylbenzoate decarboxylase are required for plastoquinone biosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803
Abstract
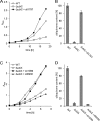
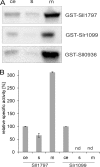
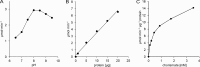
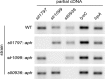
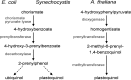
Plastoquinone is a redox active lipid that serves as electron transporter in the bifunctional photosynthetic-respiratory transport chain of cyanobacteria. To examine the role of genes potentially involved in cyanobacterial plastoquinone biosynthesis, we have focused on three Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 genes likely encoding a chorismate pyruvate-lyase (sll1797) and two 4-hydroxy-3-solanesylbenzoate decarboxylases (slr1099 and sll0936). The functions of the encoded proteins were investigated by complementation experiments with Escherichia coli mutants, by the in vitro enzyme assays with the recombinant proteins, and by the development of Synechocystis sp. single-gene knock-out mutants. Our results demonstrate that sll1797 encodes a chorismate pyruvate-lyase. In the respective knock-out mutant, plastoquinone was hardly detectable, and the mutant required 4-hydroxybenzoate for growth underlining the importance of chorismate pyruvate-lyase to initiate plastoquinone biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. The recombinant Slr1099 protein displayed decarboxylase activity and catalyzed in vitro the decarboxylation of 4-hydroxy-3-prenylbenzoate with different prenyl side chain lengths. In contrast to Slr1099, the recombinant Sll0936 protein did not show decarboxylase activity regardless of the conditions used. Inactivation of the sll0936 gene in Synechocystis sp., however, caused a drastic reduction in the plastoquinone content to levels very similar to those determined in the slr1099 knock-out mutant. This proves that not only slr1099 but also sll0936 is required for plastoquinone synthesis in the cyanobacterium. In summary, our data demonstrate that cyanobacteria produce plastoquinone exclusively via a pathway that is in the first reaction steps almost identical to ubiquinone biosynthesis in E. coli with conversion of chorismate to 4-hydroxybenzoate, which is then prenylated and decarboxylated.
Keywords: 4-Hydroxy-3-prenylbenzoate Decarboxylase; Chorismate Pyruvate-Lyase; Cyanobacteria; Isoprenoid; Mutant; Photosynthesis; Plastoquinone; Quinones; Ubiquinone.
Figures



References
-
- Schultze M., Forberich B., Rexroth S., Dyczmons N. G., Roegner M., Appel J. (2009) Localization of cytochrome b6f complexes implies an incomplete respiratory chain in cytoplasmic membranes of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 1479–1485 - PubMed
-
- Scherer S., Alpes I., Sadowski H., Böger P. (1988) Ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase is the respiratory NADPH dehydrogenase of the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 267, 228–235 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

