Increased ribozyme activity in crowded solutions
- PMID: 24337582
- PMCID: PMC3908428
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527861
Increased ribozyme activity in crowded solutions
Abstract
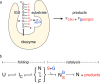
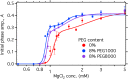
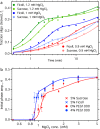
Noncoding RNAs must function in the crowded environment of the cell. Previous small-angle x-ray scattering experiments showed that molecular crowders stabilize the structure of the Azoarcus group I ribozyme, allowing the ribozyme to fold at low physiological Mg(2+) concentrations. Here, we used an RNA cleavage assay to show that the PEG and Ficoll crowder molecules increased the biochemical activity of the ribozyme, whereas sucrose did not. Crowding lowered the Mg(2+) threshold at which activity was detected and increased total RNA cleavage at high Mg(2+) concentrations sufficient to fold the RNA in crowded or dilute solution. After correcting for solution viscosity, the observed reaction rate was proportional to the fraction of active ribozyme. We conclude that molecular crowders stabilize the native ribozyme and favor the active structure relative to compact inactive folding intermediates.
Keywords: Macromolecular Crowding; PEG; RNA Catalysis; RNA Folding; Ribozyme; X-ray Scattering.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular crowding overcomes the destabilizing effects of mutations in a bacterial ribozyme.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(2):1170-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1335. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25541198 Free PMC article.
-
Crowders perturb the entropy of RNA energy landscapes to favor folding.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Jul 10;135(27):10055-63. doi: 10.1021/ja4030098. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23773075 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular crowding favors reactivity of a human ribozyme under physiological ionic conditions.Biochemistry. 2013 Nov 19;52(46):8187-97. doi: 10.1021/bi400816s. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24187989 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular crowding and RNA catalysis.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Oct 14;18(39):7724-7739. doi: 10.1039/d0ob01695k. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32914154 Review.
-
Structure-function studies of the hammerhead ribozyme.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1997 Dec;1(4):532-6. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(97)80049-x. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1997. PMID: 9667883 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative RNA Conformations: Companion or Combatant.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 23;13(11):1930. doi: 10.3390/genes13111930. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligomerization of a Bimolecular Ribozyme Modestly Rescues its Structural Defects that Disturb Interdomain Assembly to Form the Catalytic Site.J Mol Evol. 2018 Aug;86(7):431-442. doi: 10.1007/s00239-018-9862-8. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Mol Evol. 2018. PMID: 30105586
-
Vesicle encapsulation stabilizes intermolecular association and structure formation of functional RNA and DNA.Curr Biol. 2022 Jan 10;32(1):86-96.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.10.047. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 34762821 Free PMC article.
-
Amplification of RNA by an RNA polymerase ribozyme.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 30;113(35):9786-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610103113. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27528667 Free PMC article.
-
The structural stability and catalytic activity of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides in the presence of organic solvents.Biophys Rev. 2016 Mar;8(1):11-23. doi: 10.1007/s12551-015-0188-0. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Biophys Rev. 2016. PMID: 28510143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellis R. J. (2001) Macromolecular crowding: obvious but underappreciated. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 597–604 - PubMed
-
- Minton A. P. (1981) Excluded volume as a determinant of macromolecular structure and reactivity. Biopolymers 20, 2093–2120
-
- Minton A. P. (2000) Implications of macromolecular crowding for protein assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10, 34–39 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

