Aged mice are unable to mount an effective myeloid response to sepsis
- PMID: 24337739
- PMCID: PMC3884685
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302109
Aged mice are unable to mount an effective myeloid response to sepsis
Abstract
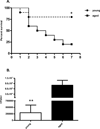
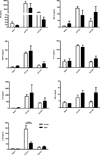
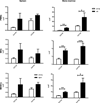
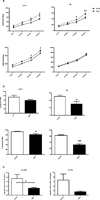
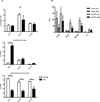
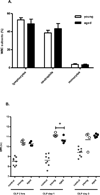
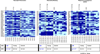
The elderly have increased morbidity and mortality following sepsis; however, the cause(s) remains unclear. We hypothesized that these poor outcomes are due in part to defects in innate immunity, rather than to an exaggerated early inflammatory response. Young (6-12 wk) or aged (20-24 mo) mice underwent polymicrobial sepsis, and subsequently, the aged mice had increased mortality and defective peritoneal bacterial clearance compared with young mice. No differences were found in the magnitude of the plasma cytokine responses. Although septic aged mice displayed equivalent or increased numbers of circulating, splenic, and bone marrow myeloid cells, some of these cells exhibited decreased phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species production, and chemotaxis. Blood leukocyte gene expression was less altered in aged versus young mice 1 d after sepsis. Aged mice had a relative inability to upregulate gene expression of pathways related to neutrophil-mediated protective immunity, chemokine/chemokine receptor binding, and responses to exogenous molecules. Expression of most MHC genes remained more downregulated in aged mice at day 3. Despite their increased myeloid response to sepsis, the increased susceptibility of aged mice to sepsis appears not to be due to an exaggerated inflammatory response, but rather, a failure to mount an effective innate immune response.
Figures
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Critical care medicine. 2006;34:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Sands KE, Bates DW, Lanken PN, Graman PS, Hibberd PL, Kahn KL, Parsonnet J, Panzer R, Orav EJ, Snydman DR, Black E, Schwartz JS, Moore R, Johnson BL, Jr., Platt R. Epidemiology of sepsis syndrome in 8 academic medical centers. Jama. 1997;278:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: a trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Critical care medicine. 2007;35:1244–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

