Thymic medullary epithelium and thymocyte self-tolerance require cooperation between CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L costimulatory pathways
- PMID: 24337745
- PMCID: PMC3897934
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302550
Thymic medullary epithelium and thymocyte self-tolerance require cooperation between CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L costimulatory pathways
Abstract
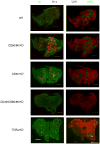
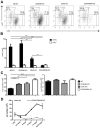
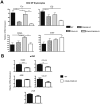
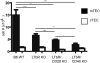
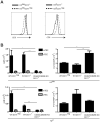
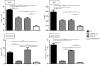
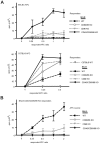
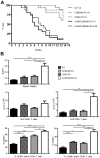
A critical process during thymic development of the T cell repertoire is the induction of self-tolerance. Tolerance in developing T cells is highly dependent on medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTEC), and mTEC development in turn requires signals from mature single-positive thymocytes, a bidirectional relationship termed thymus crosstalk. We show that CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L costimulatory interactions, which mediate negative selection and self-tolerance, upregulate expression of LTα, LTβ, and receptor activator for NF-κB in the thymus and are necessary for medullary development. Combined absence of CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L results in profound deficiency in mTEC development comparable to that observed in the absence of single-positive thymocytes. This requirement for costimulatory signaling is maintained even in a TCR transgenic model of high-affinity TCR-ligand interactions. CD4 thymocytes maturing in the altered thymic epithelial environment of CD40/CD80/86 knockout mice are highly autoreactive in vitro and are lethal in congenic adoptive transfer in vivo, demonstrating a critical role for these costimulatory pathways in self-tolerance as well as thymic epithelial development. These findings demonstrate that cooperativity between CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L pathways is required for normal medullary epithelium and for maintenance of self-tolerance in thymocyte development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L Interactions Promote Thymic Tolerance by Regulating Medullary Epithelial Cell and Thymocyte Development.Crit Rev Immunol. 2015;35(1):59-76. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2015012501. Crit Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25746048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggressive skin allograft rejection in CD28-/- mice independent of the CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway.Transpl Immunol. 2001 Oct;9(1):13-7. doi: 10.1016/s0966-3274(01)00043-0. Transpl Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11680567
-
Antigen recognition by autoreactive CD4⁺ thymocytes drives homeostasis of the thymic medulla.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052591. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300712 Free PMC article.
-
CD40 ligand functions non-cell autonomously to promote deletion of self-reactive thymocytes.J Immunol. 2002 Mar 15;168(6):2759-65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2759. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11884443
-
Thymic microenvironments for T-cell repertoire formation.Adv Immunol. 2008;99:59-94. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00603-2. Adv Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19117532 Review.
Cited by
-
LKB1 expressed in dendritic cells governs the development and expansion of thymus-derived regulatory T cells.Cell Res. 2019 May;29(5):406-419. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0161-8. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30940876 Free PMC article.
-
Medullary thymic epithelial NF-kB-inducing kinase (NIK)/IKKα pathway shapes autoimmunity and liver and lung homeostasis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 17;116(38):19090-19097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901056116. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31481626 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic Crosstalk: An Overview of the Complex Cellular Interactions that Control the Establishment of T-Cell Tolerance.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1471:177-197. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-77921-3_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40067587 Review.
-
Dual roles for LUBAC signaling in thymic epithelial cell development and survival.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Oct;28(10):2946-2956. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00850-8. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 34381167 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of molecule CD28 and CD38 on CD4⁺/CD8⁺ T lymphocytes in thymus and spleen elicited by Schistosoma japonicum infection in mice model.Parasitol Res. 2015 Aug;114(8):3047-58. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4507-y. Epub 2015 May 24. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 26002824
References
-
- Heino M, Peterson P, Kudoh J, Nagamine K, Lagerstedt A, Ovod V, Ranki A, Rantala I, Nieminen M, Tuukkanen J, Scott HS, Antonarakis SE, Shimizu N, Krohn K. Autoimmune regulator is expressed in the cells regulating immune tolerance in thymus medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;257:821–825. - PubMed
-
- Derbinski J, Schulte A, Kyewski B, Klein L. Promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells mirrors the peripheral self. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:1032–1039. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen Z, Berzins SP, Turley SJ, von Boehmer H, Bronson R, Dierich A, Benoist C, Mathis D. Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science. 2002;298:1395–1401. - PubMed
-
- Shores EW, Van Ewijk W, Singer A. Disorganization and restoration of thymic medullary epithelial cells in T cell receptor-negative scid mice: evidence that receptor-bearing lymphocytes influence maturation of the thymic microenvironment. Eur J Immunol. 1991;21:1657–1661. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

