The clinical, radiological, and bronchoscopic findings and outcomes in patients with benign tracheobronchial tumors
- PMID: 24339291
- PMCID: PMC3874910
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.84
The clinical, radiological, and bronchoscopic findings and outcomes in patients with benign tracheobronchial tumors
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated the characteristics of and treatment outcomes in patients with benign tracheobronchial tumors.
Materials and methods: We reviewed the records of patients with benign tracheobronchial tumors who underwent bronchoscopic intervention with mechanical removal and Nd: YAG laser cauterization, and evaluated the characteristics and treatment outcomes of 55 patients with hamartomas, leiomyomas, papillomas, typical carcinoids, or schwannomas seen between April 1999 and July 2012.
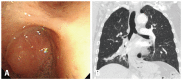
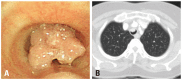
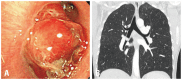
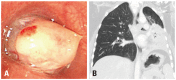
Results: The most common tumors were hamartoma (n=24), leiomyoma (n=16), papilloma (n=7), typical carcinoid (n=5), and schwannoma (n=3). Forty-one patients (75%) had symptoms. On chest computed tomography, 35 patients (64%) had round or ovoid lesions, accompanied by atelectasis (n=26, 47%) or obstructive pneumonia (n=17, 31%). Fatty components (n=9, 16%) and calcifications (n=7, 13%) were observed only in hamartomas, leiomyomas, and typical carcinoids. At bronchoscopy, the typical findings were categorized according to tumor shape, surface, color, and visible vessels. Fifty (91%) patients underwent complete resection. Forty patients (73%) achieved successful bronchoscopic removal defined as complete resection without complications or recurrence. Recurrences occurred in four papillomas, one leiomyoma, and one typical carcinoid. The proportions of tumor types (p=0.029) differed between the successful and unsuccessful removal groups, and a pedunculated base (p<0.001) and no spontaneous bleeding (p=0.037) were more frequent in the successful removal group.
Conclusion: We described clinical, radiological, and typical bronchoscopic findings in patients with benign tracheobronchial tumors; these findings might help to differentiate such tumors. Bronchoscopic intervention was a useful treatment modality, and tumor type, pedunculated base, and vascularity may influence successful tumor removal.
Keywords: Benign tracheobronchial tumors; bronchoscopy; intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Arrigoni MG, Woolner LB, Bernatz PE, Miller WE, Fontana RS. Benign tumors of the lung. A ten-year surgical experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1970;60:589–599. - PubMed
-
- Thomas R, Christopher DJ, Thangakunam B, Samuel R. Tracheal schwannoma as a mimic of bronchial asthma. Singapore Med J. 2012;53:e95–e96. - PubMed
-
- Takeda S, Hashimoto T, Kusu T, Kawamura T, Nojiri T, Funakoshi Y, et al. Management and surgical resection for tracheobronchial tumors institutional experience with 12 patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007;6:484–489. - PubMed
-
- Stevic R, Milenkovic B, Stojsic J, Pesut D, Ercegovac M, Jovanovic D. Clinical and radiological manifestations of primary tracheobronchial tumours: a single centre experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2012;41:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Otani Y, Yoshida I, Kawashima O, Yamagishi T, Ishikawa S, Ohtaki A, et al. Benign tumors of the lung: a 20-year surgical experience. Surg Today. 1997;27:310–312. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

