Musculoskeletal and rheumatological disorders in HIV infection: Experience in a tertiary referral center
- PMID: 24339461
- PMCID: PMC3841660
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7184.120542
Musculoskeletal and rheumatological disorders in HIV infection: Experience in a tertiary referral center
Abstract
Background: Musculoskeletal involvement in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected patients are important disease manifestations, responsible for increased morbidity and also decreased quality of life.
Objectives: To study the spectrum of different musculoskeletal involvement in HIV infected patients and its impact on quality of life.
Patients and methods: Three hundred (n = 300) HIV-1 reactive patients were evaluated in respect to different musculoskeletal involvement including the quality of life from January 2010 to January 2011.
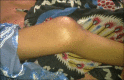
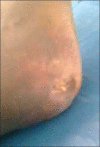
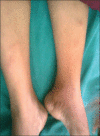
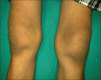
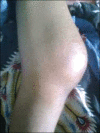
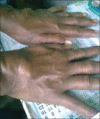
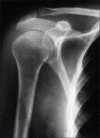
Results: Male to female ratio was 11:1 with a mean age of 35 (±6.4) years and mean duration of the disease was 3 (±1.54) years. Majority of cases were truck drivers, motel workers, and jewelry workers. Musculoskeletal disorders were observed in a total of 190 cases (63.33%). The spectrum of musculoskeletal involvement was: Body ache in 140 (46.7%), arthralgia in 80 (26.7%), mechanical low back pain in 25 (8.3%), osteoporosis in 20 (6.7%), painful articular syndrome in 10 (3.3%), hypertrophic osteoarthropathy in two (0.7%), pyomyositis in two (0.7%), osteomyelitis in one (0.3%), and avascular bone necrosis in one patient (0.3%). Rheumatologic disorders associated were: Reactive arthritis in seven (2.3%), fibromyalgia in four (1.3%), septic arthritis in three (1%), acute gout in three (1%), spondyloarthropathy in two (0.7%), rheumatoid arthritis in two (0.7%), dermatomyositis in one (0.3%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in one patient (0.3%). But HIV associated arthritis and diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome (DILS) were not detected. Most of the patients had decreased quality of life.
Conclusions: Musculoskeletal involvement was common in HIV patients causing increased morbidity, so early detection and timely intervention is essential to improve quality of life.
Keywords: Human immunodeficiency virus infection; musculoskeletal disorder; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS: Fact sheet; AIDS Epidemic in Asia. 2004
-
- Calabrese LH. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993;19:477–88. - PubMed
-
- Medina-Rodriguez F, Guzman C, Jara LJ, Hermida C, Alboukrek D, Cervera H, et al. Rheumatic manifestations in human immunodeficiency virus positive and negative individuals: A study of 2 populations with similar risk factors. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:1880–4. - PubMed
-
- Berman A, Espinoza LR, Diaz JD, Aguilar JL, Rolando T, Vasey FB, et al. Rheumatic manifestation of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Med. 1988;85:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez W. Musculoskeletal manifestations of HIV disease. J Watch HIV/AIDS Clin Care. 1998 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

