Opercular myoclonic-anarthric status epilepticus: A report of two cases
- PMID: 24339580
- PMCID: PMC3841601
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-2327.120470
Opercular myoclonic-anarthric status epilepticus: A report of two cases
Abstract
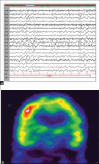
Opercular myoclonic-anarthric status epilepticus (OMASE) is an uncommon disorder of diverse etiology. This condition is characterized by fluctuating cortical dysarthria associated with epileptic myoclonus involving glossopharyngeal musculature bilaterally. We report two cases of OMASE of vascular etiology in adults. In both patients, ictally clonic expression was consistent with epilepsia partialis continua and bilateral, symmetrical involvement of soft palate in one patient and tongue, lips, chin and inferior jaw in both patients due to bilateral projections of the inferior corticonuclear pathways. The inferior rolandic area of dominant and high frontal region in non-dominant hemispheres were involved by an epileptogenic lesion of vascular etiology, which was confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging of brain and single photon emission computerized tomography. Carotid Doppler study showed thrombosis of internal carotid artery in both patients, suggestive of an embolic origin. Early recognition of OMASE is important for early management of carotid occlusive disease.
Keywords: Epilepsia partialis continua; glossopharyngeal musculature; opercular myoclonic status epilepticus-anarthria; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Thomas JE, Reagan TJ, Klass DW. Epilepsia partialis continua. A review of 32 cases. Arch Neurol. 1977;34:266–75. - PubMed
-
- Tatum WO, Sperling MR, Jacobstein JG. Epileptic palatal myoclonus. Neurology. 1991;41:1305–6. - PubMed
-
- Thomas P, Borg M, Suisse G, Chatel M. Opercular myoclonic-anarthric status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1995;36:281–9. - PubMed
-
- Emre M. Palatal myoclonus occurring during complex partial status epilepticus. J Neurol. 1992;239:228–30. - PubMed
-
- Nayak D, Abraham M, Kesavadas C, Radhakrishnan K. Lingual epilepsia partialis continua in Rasmussen's encephalitis. Epileptic Disord. 2006;8:114–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

