Pediatric index of mortality 2 score as an outcome predictor in pediatric Intensive Care Unit in India
- PMID: 24339640
- PMCID: PMC3841491
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.120320
Pediatric index of mortality 2 score as an outcome predictor in pediatric Intensive Care Unit in India
Abstract
Background and aims: Pediatric index of mortality (PIM) 2 score is one of the severity scoring systems being used for predicting outcome of patients admitted to intensive care units (ICUs). The aim of the present study was to evaluate the usefulness of PIM2 score in predicting mortality in a tertiary care pediatric ICU (PICU) and to assess the associated factors in predicting mortality such as presence of shock, need for assisted ventilation and Glasgow coma scale <8.
Materials and methods: This was a prospective observation study done at tertiary care PICU from May 2011 to July 2011. Consecutive 119 patients admitted to PICU (aged 1 month to 12 years) were enrolled in the study. PIM2 scoring was done for all patients. The outcome was recorded as death or discharge. The associated factors for mortality were analyzed with SPSS 17.
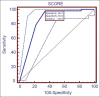
Results: PIM2 score discriminated between death and survival at a 99.8 cut-off, with area under receiver operating characteristic curve 0.843 with 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.765, 0.903). Most patients were referred late to this hospital, which explains higher death rate (46.2%), lesser length of hospital stay (mean 2.98 days) in the mortality group, and increased rate of mechanical ventilation (68.1%). Presence of shock was independently associated with mortality, as evidenced by binary logistic regression.
Conclusion: PIM2 score discriminated well between survivors and death at PICU. Presence of shock was significantly associated with mortality.
Keywords: Mortality; pediatric index of mortality 2 score; shock; ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance of Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM), Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM), and PIM2 in a pediatric intensive care unit in a developing country.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2006 Jul;7(4):356-61. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000227105.20897.89. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 16738502
-
Validation of pediatric index of mortality-2 scoring system in a single pediatric intensive care unit in iran.Iran J Pediatr. 2012 Dec;22(4):481-6. Iran J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23429969 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) III Score in Predicting Mortality Outcomes in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in Karachi.Cureus. 2020 Mar 31;12(3):e7489. doi: 10.7759/cureus.7489. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32368422 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of pSOFA with PRISM III and PIM 2 as Predictors of Outcome in a Tertiary Care Pediatric ICU: A Prospective Cross-sectional Study.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024 Aug;28(8):796-801. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24772. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39239185 Free PMC article.
-
Application of pediatric index of mortality version 2: score in pediatric intensive care unit in an African developing country.Pan Afr Med J. 2014 Mar 11;17:185. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2014.17.185.2818. eCollection 2014. Pan Afr Med J. 2014. PMID: 25396011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Pediatric Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Pediatric Risk of Mortality III Score as Mortality Prediction in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit.Cureus. 2022 Jan 9;14(1):e21055. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21055. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35155020 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Sequential Organ Assessment Score: A Comprehensive Review of the Prognostic Marker in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit.Cureus. 2024 May 10;16(5):e60034. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60034. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38854197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Fluid Balance as Predictor of Length of Assisted Mechanical Ventilation in Children Admitted to Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU).Int J Pediatr. 2022 Mar 20;2022:2090323. doi: 10.1155/2022/2090323. eCollection 2022. Int J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35356099 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of urine albumin creatinine ratio with the pediatric index of mortality 2 score for prediction of pediatric intensive care unit outcomes.Ir J Med Sci. 2021 Nov;190(4):1481-1485. doi: 10.1007/s11845-021-02755-4. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Ir J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34499310 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the pediatric risk of mortality, pediatric index of mortality, and pediatric index of mortality 2 models in a pediatric intensive care unit in China: A validation study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(14):e6431. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006431. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28383407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marik PE, Varon J. Severity scoring and outcome assessment. Computerized predictive models and scoring systems. Crit Care Clin. 1999;15:633–46. - PubMed
-
- Rogers J, Fuller HD. Use of daily Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II scores to predict individual patient survival rate. Crit Care Med. 1994;22:1402–5. - PubMed
-
- Wolfler A, Silvani P, Musicco M, Salvo I Italian Pediatric Sepsis Study (SISPe) Group. Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 score in Italy: A multicenter, prospective, observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:1407–13. - PubMed
-
- Slater A, Shann F, Pearson G Paediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) Study Group. PIM2: A revised version of the Paediatric Index of Mortality. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29:278–85. - PubMed
-
- DiCarlo J, Frankel LR. Scoring systems and predictors of mortality. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 18th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Publishers; 2007. p. 387.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical