Accidental phosgene gas exposure: A review with background study of 10 cases
- PMID: 24339660
- PMCID: PMC3841534
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2700.120372
Accidental phosgene gas exposure: A review with background study of 10 cases
Abstract
Here, authors present a review on clinical presentation and management of exposure of phosgene gas after reviewing the literature by searching with keywords phosgene exposure on Google, Cochrane, Embase and PubMed with a background of experience gained from 10 patients who were admitted to our institute after an accidental phosgene exposure in February 2011 nearby a city in India. Phosgene is a highly toxic gas, occupational workers may have accidental exposure. The gas can also be generated inadvertently during fire involving plastics and other chemicals and solvents containing chlorine, which is of concern to emergency responders. Phosgene inhalation may cause initially symptoms of respiratory tract irritation, patients feel fine thereafter, and then die of choking a day later because of build up of fluid in the lungs (delayed onset non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema). Phosgene exposure is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Patients with a history of exposure should be admitted to the hospital for a minimum of 24 h for observation because of the potential for delayed onset respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; N-acetyl-cysteine; phosgene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
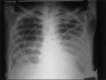
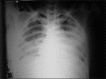
Similar articles
-
Acute accidental phosgene poisoning.BMJ Case Rep. 2012 Apr 2;2012:bcr1120115233. doi: 10.1136/bcr.11.2011.5233. BMJ Case Rep. 2012. PMID: 22602834 Free PMC article.
-
Phosgene inhalation toxicity: Update on mechanisms and mechanism-based treatment strategies.Toxicology. 2021 Feb 28;450:152682. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152682. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 33484734 Review.
-
Accidental inhalation injury of phosgene gas leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome.Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2012 May;16(2):88-9. doi: 10.4103/0019-5278.107088. Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2012. PMID: 23580841 Free PMC article.
-
The temporal profile of cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in mice exposed to the industrial gas phosgene.Inhal Toxicol. 2003 Jun;15(7):687-700. doi: 10.1080/08958370390197254. Inhal Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12754690
-
Phosgene-Induced acute lung injury: Approaches for mechanism-based treatment strategies.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 2;13:917395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.917395. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35983054 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A practically simple, catalyst free and scalable synthesis of N-substituted ureas in water.RSC Adv. 2018 Jun 13;8(38):21585-21595. doi: 10.1039/c8ra03761b. eCollection 2018 Jun 8. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539945 Free PMC article.
-
A Rapid, Highly Sensitive and Selective Phosgene Sensor Based on 5,6-Pinenepyridine.Chemistry. 2022 Oct 4;28(55):e202201772. doi: 10.1002/chem.202201772. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 35731617 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-modifying treatment of chemical threat agent-induced acute lung injury.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020 Nov;1480(1):14-29. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14438. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020. PMID: 32726497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosgene inhalation causes hemolysis and acute lung injury.Toxicol Lett. 2019 Sep 15;312:204-213. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.04.019. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Toxicol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31047999 Free PMC article.
-
Biobased polyurethanes for biomedical applications.Bioact Mater. 2020 Oct 15;6(4):1083-1106. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.10.002. eCollection 2021 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33102948 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hardy E. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopaedia of Chemical Technology. 2nd Ed. Supplement. 1971. Phosgene; pp. 674–83.
-
- Chemical Profiles: Phosgene. Washington D.C. 20460, USA: United States Environmental Protection Agency; 1985. Dec, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) p. 4.
-
- Eckert WG. Mass deaths by gas or chemical poisoning. A historical perspective. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1991;12:119–25. - PubMed
-
- Bradley BL, Unger KM. Phosgene inhalation: A case report. Tex Med. 1982;78:51–3. - PubMed
-
- Goldfrank LR, Flomenbaum NE, Lewin NA, Weisman RS, Howland MA, Hoffman RS. Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies. 5th ed. East Norwalk, CT: Appleton and Lange; 1994. pp. 1–20.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

