A clinical trial and extension study of infliximab in Korean patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment
- PMID: 24339699
- PMCID: PMC3857365
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.12.1716
A clinical trial and extension study of infliximab in Korean patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment
Abstract
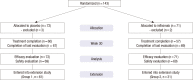
Currently, infliximab is given for disease control for active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients despite methotrexate treatment. However, the efficacy and safety of infliximab in Korean patients has not been assessed appropriately. Therefore, we performed placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study and extension study. One-hundred forty-three patients with active RA were randomized to receive placebo or infliximab 3 mg/kg intravenously at week 0, 2, 6, 14, and 22 with methotrexate maintenance. Primary endpoint was American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria (ACR20) at 30 week. After the clinical trial, patients on placebo (Group 1) and patients on infliximab who showed ACR20 response (Group 2) were treated with infliximab through another 84 week for evaluation of safety. During clinical trial, patients in infliximab group showed higher ACR20 at week 30 than patients in placebo group (50.1% vs 30.6%, P=0.014). A total of 92 patients participated in the extension study. The maintenance rate of infliximab was 62.0% at 84 weeks of extension study. The overall rate of adverse events was not different between Group 1 and Group 2. In Korean patients with active RA despite methotrexate treatment, infliximab in combination with methotrexate is effective and the long-term treatment with infliximab is well tolerated. (ClinicalTrials.gov No. NCT00202852, NCT00732875).
Keywords: Adverse Event; Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Efficacy; Extension Study; Infliximab; Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Chantry D, Haworth C, Turner M, Abney E, Buchan G, Barrett K, Barkley D, Chu A. Cytokine production in the rheumatoid joint: implications for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990;49:480–486. - PubMed
-
- Cope AP, Aderka D, Doherty M, Engelmann H, Gibbons D, Jones AC, Brennan FM, Maini RN, Wallach D, Feldmann M. Increased levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in the sera and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:1160–1169. - PubMed
-
- Knight DM, Trinh H, Le J, Siegel S, Shealy D, McDonough M, Scallon B, Moore MA, Vilcek J, Daddona P, et al. Construction and initial characterization of a mouse-human chimeric anti-TNF antibody. Mol Immunol. 1993;30:1443–1453. - PubMed
-
- Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Kalden JR, Antoni C, Smolen JS, Leeb B, Breedveld FC, Macfarlane JD, Bijl H, et al. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994;344:1105–1110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical