The regulation of the autophagic network and its implications for human disease
- PMID: 24339733
- PMCID: PMC3858585
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6666
The regulation of the autophagic network and its implications for human disease
Abstract
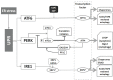
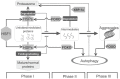
Autophagy has attracted a lot of attention in recent years. More and more proteins and signaling pathways have been discovered that somehow feed into the autophagy regulatory pathways. Regulation of autophagy is complex and condition-specific, and in several diseases, autophagic fluxes are changed. Here, we review the most well-established concepts in this field as well as the reported signaling pathways or components which steer the autophagy machinery. Furthermore, we will highlight how autophagic fluxes are changed in various diseases either as cause for or as response to deal with an altered cellular homeostasis and how modulation of autophagy might be used as potential therapy for such diseases.
Keywords: ATGs; Autophagy; FOXO1; HSF1; Heat Shock Proteins (HSP); Human diseases.; UPR; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
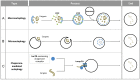
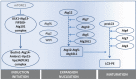
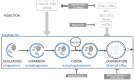
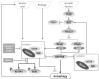
References
-
- Zhao Y, Yang J, Liao W, Liu X, Zhang H, Wang S. et al. Cytosolic FoxO1 is essential for the induction of autophagy and tumour suppressor activity. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(7):665–75. - PubMed
-
- Nakatogawa H, Ohbayashi S, Sakoh-Nakatogawa M, Kakuta S, Suzuki SW, Kirisako H. et al. The Autophagy-related Protein Kinase Atg1 Interacts with the Ubiquitin-like Protein Atg8 via the Atg8 Family Interacting Motif to Facilitate Autophagosome Formation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(34):28503–7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, Ohsumi Y. Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(7):458–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

