A downy mildew effector attenuates salicylic acid-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis by interacting with the host mediator complex
- PMID: 24339748
- PMCID: PMC3858237
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001732
A downy mildew effector attenuates salicylic acid-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis by interacting with the host mediator complex
Erratum in
- PLoS Biol. 2014 Jun;12(6):e1001909
-
Correction: A Downy Mildew Effector Attenuates Salicylic Acid-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis by Interacting with the Host Mediator Complex.PLoS Biol. 2016 Mar 2;14(3):e1002408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002408. eCollection 2016 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2016. PMID: 26934709 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
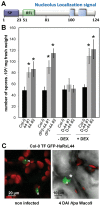
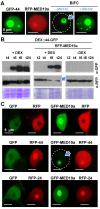
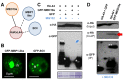
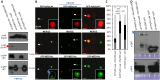
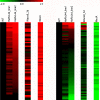
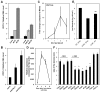
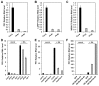
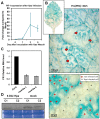
Plants are continually exposed to pathogen attack but usually remain healthy because they can activate defences upon perception of microbes. However, pathogens have evolved to overcome plant immunity by delivering effectors into the plant cell to attenuate defence, resulting in disease. Recent studies suggest that some effectors may manipulate host transcription, but the specific mechanisms by which such effectors promote susceptibility remain unclear. We study the oomycete downy mildew pathogen of Arabidopsis, Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (Hpa), and show here that the nuclear-localized effector HaRxL44 interacts with Mediator subunit 19a (MED19a), resulting in the degradation of MED19a in a proteasome-dependent manner. The Mediator complex of ∼25 proteins is broadly conserved in eukaryotes and mediates the interaction between transcriptional regulators and RNA polymerase II. We found MED19a to be a positive regulator of immunity against Hpa. Expression profiling experiments reveal transcriptional changes resembling jasmonic acid/ethylene (JA/ET) signalling in the presence of HaRxL44, and also 3 d after infection with Hpa. Elevated JA/ET signalling is associated with a decrease in salicylic acid (SA)-triggered immunity (SATI) in Arabidopsis plants expressing HaRxL44 and in med19a loss-of-function mutants, whereas SATI is elevated in plants overexpressing MED19a. Using a PR1::GUS reporter, we discovered that Hpa suppresses PR1 expression specifically in cells containing haustoria, into which RxLR effectors are delivered, but not in nonhaustoriated adjacent cells, which show high PR1::GUS expression levels. Thus, HaRxL44 interferes with Mediator function by degrading MED19, shifting the balance of defence transcription from SA-responsive defence to JA/ET-signalling, and enhancing susceptibility to biotrophs by attenuating SA-dependent gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Oomycetes: attacking the mediator.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014 Feb;12(2):74-5. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3208. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24429412 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Expression profiling during arabidopsis/downy mildew interaction reveals a highly-expressed effector that attenuates responses to salicylic acid.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Oct 16;10(10):e1004443. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004443. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25329884 Free PMC article.
-
Oomycetes: attacking the mediator.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014 Feb;12(2):74-5. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3208. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24429412 No abstract available.
-
Arabidopsis downy mildew effector HaRxL106 suppresses plant immunity by binding to RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1.New Phytol. 2018 Oct;220(1):232-248. doi: 10.1111/nph.15277. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 30156022 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaloperonospora Arabidopsidis as a pathogen model.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2010;48:329-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-094422. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2010. PMID: 19400636 Review.
-
Fine-Tuning Plant Defence Signalling: Salicylate versus Jasmonate.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2006 Jan;8(1):1-10. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-872705. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2006. PMID: 16435264 Review.
Cited by
-
A rust fungal effector binds plant DNA and modulates transcription.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 3;8(1):14718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32825-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30283062 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear effectors of plant pathogens: Distinct strategies to be one step ahead.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Jun;24(6):637-650. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13315. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36942744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mediator Complex: A Central Coordinator of Plant Adaptive Responses to Environmental Stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 31;23(11):6170. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116170. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valsa mali Pathogenic Effector VmPxE1 Contributes to Full Virulence and Interacts With the Host Peroxidase MdAPX1 as a Potential Target.Front Microbiol. 2018 Apr 25;9:821. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00821. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29922244 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Trends in Molecular Interactions between Plants and the Broad Host Range Fungal Pathogens Botrytis cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Mar 31;7:422. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00422. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27066056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444: 323–329. - PubMed
-
- Dangl JL, Jones JD (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411: 826–833. - PubMed
-
- Robert-Seilaniantz A, Grant M, Jones JD (2011) Hormone crosstalk in plant disease and defense: more than just jasmonate-salicylate antagonism. Annu Rev Phytopathol 49: 317–343. - PubMed
-
- Djamei A, Schipper K, Rabe F, Ghosh A, Vincon V, et al. (2011) Metabolic priming by a secreted fungal effector. Nature 478: 395–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

