Hyperactivation of the habenula as a link between depression and sleep disturbance
- PMID: 24339810
- PMCID: PMC3857532
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00826
Hyperactivation of the habenula as a link between depression and sleep disturbance
Abstract
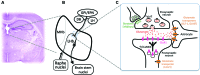
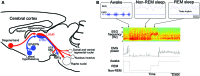
Depression occurs frequently with sleep disturbance such as insomnia. Sleep in depression is associated with disinhibition of the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Despite the coincidence of the depression and sleep disturbance, neural substrate for depressive behaviors and sleep regulation remains unknown. Habenula is an epithalamic structure regulating the activities of monoaminergic neurons in the brain stem. Since the imaging studies showed blood flow increase in the habenula of depressive patients, hyperactivation of the habenula has been implicated in the pathophysiology of the depression. Recent electrophysiological studies reported a novel role of the habenular structure in regulation of REM sleep. In this article, we propose possible cellular mechanisms which could elicit the hyperactivation of the habenular neurons and a hypothesis that dysfunction in the habenular circuit causes the behavioral and sleep disturbance in depression. Analysis of the animals with hyperactivated habenula would open the door to understand roles of the habenula in the heterogeneous symptoms such as reduced motor behavior and altered REM sleep in depression.
Keywords: depression; glutamate transporters; glutamates; habenula; monoamines; rapid eye movement sleep (REMS).
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

