Granuloma formation in pulmonary sarcoidosis
- PMID: 24339826
- PMCID: PMC3857538
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00437
Granuloma formation in pulmonary sarcoidosis
Abstract
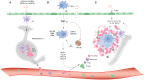
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disorder of unknown cause, affecting multiple organs, but mainly the lungs. The exact order of immunological events remains obscure. Reviewing current literature, combined with careful clinical observations, we propose a model for granuloma formation in pulmonary sarcoidosis. A tight collaboration between macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocyte subsets, initiates the first steps toward granuloma formation, orchestrated by cytokines and chemokines. In a substantial part of pulmonary sarcoidosis patients, granuloma formation becomes an on-going process, leading to debilitating disease, and sometimes death. The immunological response, determining granuloma sustainment is not well understood. An impaired immunosuppressive function of regulatory T cells has been suggested to contribute to the exaggerated response. Interestingly, therapeutical agents commonly used in sarcoidosis, such as glucocorticosteroids and anti-TNF agents, interfere with granuloma integrity and restore the immune homeostasis in autoimmune disorders. Increasing insight into their mechanisms of action may contribute to the search for new therapeutical targets in pulmonary sarcoidosis.
Keywords: T helper 1 cells; T helper 17 cells; dendritic cells; formation; granuloma; integrity; pulmonary sarcoidosis; regulatory T cells.
Figures
References
-
- Hunninghake GW, Costabel U, Ando M, Baughman R, Cordier JF, du Bois R, et al. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American thoracic society/European respiratory society/World Association of sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis (1999) 16(2):149. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

