The newly discovered cytokine IL-34 is expressed in gingival fibroblasts, shows enhanced expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines, and stimulates osteoclast differentiation
- PMID: 24339952
- PMCID: PMC3858262
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081665
The newly discovered cytokine IL-34 is expressed in gingival fibroblasts, shows enhanced expression by pro-inflammatory cytokines, and stimulates osteoclast differentiation
Abstract
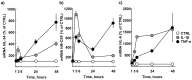
Background: Interleukin-34 (IL-34) is a recently discovered cytokine functionally overlapping macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF), a mediator of inflammation and osteoclastogenesis in bone-degenerative diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. The objective of this study was to assess the expression of IL-34 in human gingival fibroblasts and investigate if the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and Interleukin-1Β (IL-1β) modulate its expression, and moreover if IL-34 could contribute to recruitment of bone-resorbing osteoclasts.
Methods: IL-34 expression was evaluated in gingival fibroblasts by real time PCR following stimulation by TNF-α, IL-1β, and treatment with inhibitors of intracellular pathways. The formation of osteoclasts was evaluated by tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining of bone marrow macrophages treated with IL-34 or M-CSF in addition to receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL).
Results: IL-34 was expressed in gingival fibroblasts. The expression was enhanced by TNF-α and IL-1β, regulated by the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κΒ) and activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Further, IL-34 supports RANKL-induced osteoclastogensis of bone marrow macrophages, independently of M-CSF.
Summary: In conclusion, this study shows for the first time IL-34 expression in human gingival fibroblasts, stimulated by TNF-α and IL-1β, key mediators of periodontal inflammation. Furthermore, IL-34 can be substituted for M-CSF in RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. IL-34 may contribute to inflammation and osteoclastogenesis in bone-degenerative diseases such as periodontitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Hamilton JA (2008) Colony-stimulating factors in inflammation and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 8: 533–544. - PubMed
-
- Kimura K, Kitaura H, Fujii T, Ishida M, Hakami Z, et al.. (2013) An anti-c-Fms antibody inhibits osteoclastogenesis in a mouse periodontitis model. Oral Dis. - PubMed
-
- Campbell IK, Rich MJ, Bischof RJ, Hamilton JA (2000) The colony-stimulating factors and collagen-induced arthritis: exacerbation of disease by M-CSF and G-CSF and requirement for endogenous M-CSF. J Leukoc Biol 68: 144–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

