The enhanced in vivo activity of the combination of a MEK and a PI3K inhibitor correlates with [18F]-FLT PET in human colorectal cancer xenograft tumour-bearing mice
- PMID: 24339963
- PMCID: PMC3858267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081763
The enhanced in vivo activity of the combination of a MEK and a PI3K inhibitor correlates with [18F]-FLT PET in human colorectal cancer xenograft tumour-bearing mice
Abstract
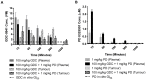
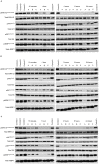
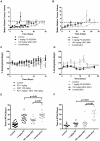
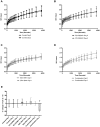
Combined targeting of the MAPK and PI3K signalling pathways in cancer may be necessary for optimal therapeutic activity. To support clinical studies of combination therapy, 3'-deoxy-3'-[(18)F]-fluorothymidine ([(18)F]-FLT) uptake measured by Positron Emission Tomography (PET) was evaluated as a non-invasive surrogate response biomarker in pre-clinical models. The in vivo anti-tumour efficacy and PK-PD properties of the MEK inhibitor PD 0325901 and the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941, alone and in combination, were evaluated in HCT116 and HT29 human colorectal cancer xenograft tumour-bearing mice, and [(18)F]-FLT PET investigated in mice bearing HCT116 xenografts. Dual targeting of PI3K and MEK induced marked tumour growth inhibition in vivo, and enhanced anti-tumour activity was predicted by [(18)F]-FLT PET scanning after 2 days of treatment. Pharmacodynamic analyses using the combination of the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 and the MEK inhibitor PD 0325901 revealed that increased efficacy is associated with an enhanced inhibition of the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, S6 and 4EBP1, compared to that observed with either single agent, and maintained inhibition of AKT phosphorylation. Pharmacokinetic studies indicated that there was no marked PK interaction between the two drugs. Together these results indicate that the combination of PI3K and MEK inhibitors can result in significant efficacy, and demonstrate for the first time that [(18)F]-FLT PET can be correlated to the improved efficacy of combined PI3K and MEK inhibitor treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Markman B, Tao JJ, Scaltriti M (2013) PI3K pathway inhibitors: better not left alone. Curr Pharm Des 19: 895–906. - PubMed
-
- Folkes AJ, Ahmadi K, Alderton WK, Alix S, Baker SJ, et al. (2008) The Identification of 2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-(4-methanesulfonyl-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-4-morpholin-4-yl-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine (GDC-0941) as a Potent, Selective, Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of Class I PI3 Kinase for the Treatment of Cancer. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51: 5522–5532. - PubMed
-
- Edgar KA, Wallin JJ, Berry M, Lee LB, Prior WW, et al. (2010) Isoform-Specific Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors Exert Distinct Effects in Solid Tumors. Cancer Research 70: 1164–1172. - PubMed
-
- Wallin JJ, Guan J, Prior WW, Lee LB, Berry L, et al. (2012) GDC-0941, a Novel Class I Selective PI3K Inhibitor, Enhances the Efficacy of Docetaxel in Human Breast Cancer Models by Increasing Cell Death In Vitro and In Vivo. Clinical Cancer Research 18: 3901–3911. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien C, Wallin JJ, Sampath D, GuhaThakurta D, Savage H, et al. (2010) Predictive Biomarkers of Sensitivity to the Phosphatidylinositol 3′ Kinase Inhibitor GDC-0941 In Breast Cancer Preclinical Models. Clinical Cancer Research 16: 3670–3683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

