AMPK activation through mitochondrial regulation results in increased substrate oxidation and improved metabolic parameters in models of diabetes
- PMID: 24339975
- PMCID: PMC3855387
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081870
AMPK activation through mitochondrial regulation results in increased substrate oxidation and improved metabolic parameters in models of diabetes
Abstract
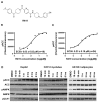
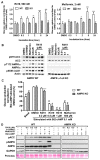
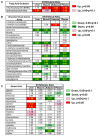
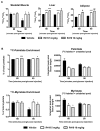
Modulation of mitochondrial function through inhibiting respiratory complex I activates a key sensor of cellular energy status, the 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Activation of AMPK results in the mobilization of nutrient uptake and catabolism for mitochondrial ATP generation to restore energy homeostasis. How these nutrient pathways are affected in the presence of a potent modulator of mitochondrial function and the role of AMPK activation in these effects remain unclear. We have identified a molecule, named R419, that activates AMPK in vitro via complex I inhibition at much lower concentrations than metformin (IC50 100 nM vs 27 mM, respectively). R419 potently increased myocyte glucose uptake that was dependent on AMPK activation, while its ability to suppress hepatic glucose production in vitro was not. In addition, R419 treatment of mouse primary hepatocytes increased fatty acid oxidation and inhibited lipogenesis in an AMPK-dependent fashion. We have performed an extensive metabolic characterization of its effects in the db/db mouse diabetes model. In vivo metabolite profiling of R419-treated db/db mice showed a clear upregulation of fatty acid oxidation and catabolism of branched chain amino acids. Additionally, analyses performed using both (13)C-palmitate and (13)C-glucose tracers revealed that R419 induces complete oxidation of both glucose and palmitate to CO2 in skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue, confirming that the compound increases mitochondrial function in vivo. Taken together, our results show that R419 is a potent inhibitor of complex I and modulates mitochondrial function in vitro and in diabetic animals in vivo. R419 may serve as a valuable molecular tool for investigating the impact of modulating mitochondrial function on nutrient metabolism in multiple tissues and on glucose and lipid homeostasis in diabetic animal models.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metformin activates AMP kinase through inhibition of AMP deaminase.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):1-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121806. Epub 2010 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21059655 Free PMC article.
-
Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action.J Clin Invest. 2001 Oct;108(8):1167-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI13505. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11602624 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids extracted from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaf improve skeletal muscle mitochondrial function by activating AMPK in type 2 diabetes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Feb 10;248:112326. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112326. Epub 2019 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31639486
-
[Regulation of energy metabolism by AMPK: a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases].Med Sci (Paris). 2006 Apr;22(4):381-8. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2006224381. Med Sci (Paris). 2006. PMID: 16597407 Review. French.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase in the regulation of hepatic energy metabolism: from physiology to therapeutic perspectives.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009 May;196(1):81-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.01970.x. Epub 2009 Feb 19. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009. PMID: 19245656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of red ginseng and ginseng leaves on the substance and energy metabolism in hypothyroidism rats.J Ginseng Res. 2017 Oct;41(4):556-565. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.11.005. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Ginseng Res. 2017. PMID: 29021704 Free PMC article.
-
Tomatine Improves Glucose Metabolism and Mitochondrial Respiration in Insulin-Resistant Hepatocyte Cell Lines AML12 and HepG2 via an AMP-Activated Protein Kinase-Dependent Pathway.Cells. 2025 Feb 23;14(5):329. doi: 10.3390/cells14050329. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072058 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Therapeutics That Induce Mitochondrial Biogenesis for the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Degenerative Diseases.J Med Chem. 2016 Dec 8;59(23):10411-10434. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00669. Epub 2016 Sep 27. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27560192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting AMPK signaling in combating ovarian cancers: opportunities and challenges.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016 Apr;48(4):301-17. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv128. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016. PMID: 26764240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin protects the rats liver against chronic intermittent hypoxia induced injury through AMP-activated protein kinase pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 28;6:34151. doi: 10.1038/srep34151. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27678302 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

