Construction and application of elastin like polypeptide containing IL-4 receptor targeting peptide
- PMID: 24339977
- PMCID: PMC3858272
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081891
Construction and application of elastin like polypeptide containing IL-4 receptor targeting peptide
Abstract
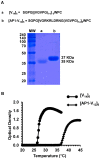
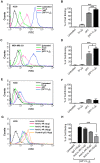
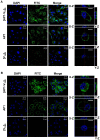
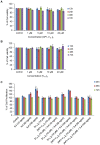
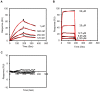
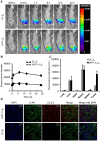
Various human solid tumors highly express IL-4 receptors which amplify the expression of some of anti-apoptotic proteins, preventing drug-induced cancer cell death. Thus, IL-4 receptor targeted drug delivery can possibly increase the therapeutic efficacy in cancer treatment. Macromolecular carriers with multivalent targeting moieties offered great advantages in cancer therapy as they not only increase the plasma half-life of the drug but also allow delivery of therapeutic drugs to the cancer cells with higher specificity, minimizing the deleterious effects of the drug on normal cells. In this study we designed a library of elastin like polypeptide (ELP) polymers containing tumor targeting AP1 peptide using recursive directional ligation method. AP1 was previously discovered as an atherosclerotic plaque and breast tumor tissue homing peptide using phage display screening method, and it can selectively bind to the interleukin 4 receptor (IL-4R). The fluorescently labeled [AP1-V12]6, an ELP polymer containing six AP1 enhanced tumor-specific targeting ability and uptake efficiency in H226 and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell lines in vitro. Surface plasmon resonance analysis showed that multivalent presentation of the targeting ligand in the ELP polymer increased the binding affinity towards IL-4 receptor compared to free peptide. The binding of [AP1-V12]6 to cancer cells was remarkably reduced when IL-4 receptors were blocked by antibody against IL-4 receptor further confirmed its binding. Importantly, the Cy5.5-labeled [AP1-V12]6 demonstrated excellent homing and longer retention in tumor tissues in MDA-MB-231 xenograft mouse model. Immunohistological studies of tumor tissues further validated the targeting efficiency of [AP1-V12]6 to tumor tissue. These results indicate that designed [AP1-V12]6 can serve as a novel carrier for selective delivery of therapeutic drugs to tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Duncan R (2006) Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat Rev Cancer 6(9): 688–701. - PubMed
-
- Dreher MR, Raucher D, Balu N, Michael Colvin O, Ludeman SM, et al. (2003) Evaluation of an elastin-like polypeptide-doxorubicin conjugate for cancer therapy. J Control Release 91(1–2): 31–43. - PubMed
-
- Gene L, Bidwell III, Izabela F, Waldemar P, Raucher D (2007) Development of elastin-like polypeptide for thermally targeted delivery of doxorubicin. Biochemical Pharmacology 73: 620–631. - PubMed
-
- Gene L, Bidwell III, Drazen R (2005) Application of thermally responsive polypeptides directed against c-Myc transcriptional function for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 4(7): 1076–1085. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

