High prevalence of illicit drug use in men who have sex with men with HIV-1 infection in Japan
- PMID: 24339982
- PMCID: PMC3858294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081960
High prevalence of illicit drug use in men who have sex with men with HIV-1 infection in Japan
Abstract
Objective: To examine the prevalence of illicit drug use among men who have sex with men (MSM) with HIV-1 infection in Japan, where the life-time prevalence of illicit drug use in the general population is only 2.9%.
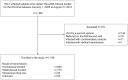
Design: A single-center cross-sectional study at a large HIV clinic in Tokyo, which treats approximately 15% of HIV-1 infected patients in Japan.
Methods: The prevalence of illicit drug use and the association of characteristics and social demographics of the patients with illicit drug use were examined. Patients who visited the clinic for the first time from 2005 to 2010 were enrolled. Relevant variables were collected using a structured interview and from the medical records. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were applied to estimate the odds of association of MSM over non-MSM HIV-infected patients with illicit drug use.
Results: 1,196 patients were enrolled. They were mostly Japanese men of relatively young age. Illicit drug use (including injection drugs) was reported by 35% of the patients (by 40% of MSM), and 4% were IDU while 5% were on methamphetamine. 2% of the population was arrested due to illicit drugs. MSM was significantly associated with illicit drug use (adjusted OR = 4.60; 95% CI, 2.88-7.36; p<0.01). Subgroup analysis of the patients stratified by three age groups (≤ 30, 31 to 40, and >40) showed that the odds of association of MSM with illicit drug use was the strongest in the youngest age group (≤ 30 years: adjusted OR = 7.56; 95% CI, 2.86-20.0; p<0.01), followed by the oldest (>40 years: adjusted OR = 6.15; 95% CI, 2.40-15.8; p<0.01), and the weakest in the group aged 31 to 40 (adjusted OR = 3.39; 95% CI, 1.73-6.63; p<0.01).
Conclusions: The prevalence of illicit drug use is high among MSM patients with HIV-1 infection in Japan. Effective intervention for illicit drug use in this population is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Similar articles
-
Nitrite inhalants use, sexual behaviors and HIV/syphilis infection among men who have sex with men in Chongqing, China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Sep 4;9(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00748-6. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 32887643 Free PMC article.
-
Illicit drug use is a significant risk factor for loss to follow up in patients with HIV-1 infection at a large urban HIV clinic in Tokyo.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 7;8(8):e72310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072310. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951307 Free PMC article.
-
Do men who have sex with men who report alcohol and illicit drug use before/during sex (chemsex) present moderate/high risk for substance use disorders?Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020 Apr 1;209:107908. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.107908. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020. PMID: 32078972
-
[Study on the prevalence of HIV infection and related risk behaviors among male new-type drug users in Qingdao, Shandong province].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 10;39(6):750-754. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.06.011. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29936741 Chinese.
-
Uncovering the epidemic of HIV among men who have sex with men in Central Asia.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013 Nov;132 Suppl 1:S17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.06.031. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013. PMID: 23906993 Review.
Cited by
-
Changing patterns of HIV epidemic in 30 years in East Asia.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2014 Jun;11(2):134-45. doi: 10.1007/s11904-014-0201-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2014. PMID: 24664878 Review.
-
Associations between Drug Use and Sexual Risk Behaviours among Men Who Have Sex with Men in Japan: Results from the Cross-Sectional LASH Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jul 2;20(13):6275. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20136275. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37444124 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Tat and Drugs of Abuse during HIV-1 Infection and Central Nervous System Disease.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jan 11;6:1512. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01512. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26793168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injection drug use and sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men: A retrospective cohort study at an HIV/AIDS referral hospital in Tokyo, 2013-2022.Epidemiol Infect. 2023 Nov 15;151:e195. doi: 10.1017/S0950268823001772. Epidemiol Infect. 2023. PMID: 37965724 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Risk Factors for Incident Syphilis among HIV-1-Infected Men Who Have Sex with Men in a Large Urban HIV Clinic in Tokyo, 2008-2015.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 16;11(12):e0168642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168642. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27992604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehman JS, Allen DM, Green TA, Onorato IM (1994) HIV infection among non-injecting drug users entering drug treatment, United States, 1989–1992. Field Services Branch. AIDS 8: 1465–1469. - PubMed
-
- Hahn RA, Onorato IM, Jones TS, Dougherty J (1989) Prevalence of HIV infection among intravenous drug users in the United States. JAMA 261: 2677–2684. - PubMed
-
- Magnani R, Sabin K, Saidel T, Heckathorn D (2005) Review of sampling hard-to-reach and hidden populations for HIV surveillance. AIDS 19 Suppl 2S67–72. - PubMed
-
- Wada K (2011) The history and current state of drug abuse in Japan. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1216: 62–72. - PubMed
-
- Tominaga M, Kawakami N, Ono Y, Nakane Y, Nakamura Y, et al. (2009) Prevalence and correlates of illicit and non-medical use of psychotropic drugs in Japan: findings from the World Mental Health Japan Survey 2002–2004. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 44: 777–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical