Development of the acoustically evoked behavioral response in larval plainfin midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus
- PMID: 24340003
- PMCID: PMC3858275
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082182
Development of the acoustically evoked behavioral response in larval plainfin midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus
Abstract
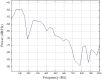
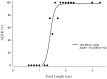
The ontogeny of hearing in fishes has become a major interest among bioacoustics researchers studying fish behavior and sensory ecology. Most fish begin to detect acoustic stimuli during the larval stage which can be important for navigation, predator avoidance and settlement, however relatively little is known about the hearing capabilities of larval fishes. We characterized the acoustically evoked behavioral response (AEBR) in the plainfin midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus, and used this innate startle-like response to characterize this species' auditory capability during larval development. Age and size of larval midshipman were highly correlated (r(2) = 0.92). The AEBR was first observed in larvae at 1.4 cm TL. At a size ≥ 1.8 cm TL, all larvae responded to a broadband stimulus of 154 dB re1 µPa or -15.2 dB re 1 g (z-axis). Lowest AEBR thresholds were 140-150 dB re 1 µPa or -33 to -23 dB re 1 g for frequencies below 225 Hz. Larval fish with size ranges of 1.9-2.4 cm TL had significantly lower best evoked frequencies than the other tested size groups. We also investigated the development of the lateral line organ and its function in mediating the AEBR. The lateral line organ is likely involved in mediating the AEBR but not necessary to evoke the startle-like response. The midshipman auditory and lateral line systems are functional during early development when the larvae are in the nest and the auditory system appears to have similar tuning characteristics throughout all life history stages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ontogeny of auditory saccular sensitivity in the plainfin midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2011 Apr;197(4):387-98. doi: 10.1007/s00359-010-0623-4. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21246201
-
Lagenar potentials of the vocal plainfin midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2019 Feb;205(1):163-175. doi: 10.1007/s00359-018-01314-0. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30635725 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory evoked potentials of utricular hair cells in the plainfin midshipman, Porichthys notatus.J Exp Biol. 2020 Sep 6;223(Pt 17):jeb226464. doi: 10.1242/jeb.226464. J Exp Biol. 2020. PMID: 32680899
-
Adaptive hearing in the vocal plainfin midshipman fish: getting in tune for the breeding season and implications for acoustic communication.Integr Zool. 2009 Mar;4(1):33-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-4877.2008.00133.x. Integr Zool. 2009. PMID: 21392275 Review.
-
Do human activities influence survival and orientation abilities of larval fishes in the ocean?Integr Zool. 2015 Jan;10(1):65-82. doi: 10.1111/1749-4877.12096. Integr Zool. 2015. PMID: 24919722 Review.
Cited by
-
Broad frequency sensitivity and complex neural coding in the larval zebrafish auditory system.Curr Biol. 2021 May 10;31(9):1977-1987.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.01.103. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 33657408 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrine control of seasonal plasticity in the auditory and vocal systems of fish.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2015 Apr;37:129-45. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.08.002. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25168757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applying appropriate frequency criteria to advance acoustic behavioural guidance systems for fish.Sci Rep. 2023 May 18;13(1):8075. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33423-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37202429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blaxter JHS, Hoss DE (1981) Startle response in herring: the effect of sound stimulus frequency, size of fish and selective interference with the acoustico-lateralis system. J Marine Biol Assoc United Kingdom 61: 871–879 10.1017/S0025315400023018 - DOI
-
- Hoss DE, Blaxter JHS (1982) Development and function of the swimbladder-inner ear-lateral line system in the Atlantic menhaden, Brevoortia tyrannus (Latrobe). J Fish Bio 20: 131–142 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1982.tb03914.x - DOI
-
- Blaxter JHS, Batty RS (1985) The development of startle responses in herring larvae. J Marine Biol Assoc United Kingdom 65: 737–750 10.1017/S0025315400052565 - DOI
-
- Blaxter JHS, Fuiman LA (1990) The role of the sensory systems of herring larvae in evading predatory fishes. J Marine Biol Assoc United Kingdom 70: 413–427 10.1017/S0025315400035505 - DOI
-
- Higgs DM, Fuiman LA (1998) Associations between sensory development and ecology in three species of clupeoid fish. Copeia 1998: 133–144.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

