Identification and characterization of a PutAMT1;1 gene from Puccinellia tenuiflora
- PMID: 24340088
- PMCID: PMC3858356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083111
Identification and characterization of a PutAMT1;1 gene from Puccinellia tenuiflora
Abstract
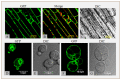
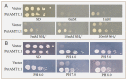
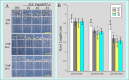
Nitrogen is one of the most important limiting factors for plant growth. However, as ammonium is readily converted into ammonia (NH3) when soil pH rises above 8.0, this activity depletes the availability of ammonium (NH4(+)) in alkaline soils, consequently preventing the growth of most plant species. The perennial wild grass Puccinellia tenuiflora is one of a few plants able to grow in soils with extremely high salt and alkaline pH (>9.0) levels. Here, we assessed how this species responds to ammonium under such conditions by isolating and analyzing the functions of a putative ammonium transporter (PutAMT1;1). PutAMT1;1 is the first member of the AMT1 (ammonium transporter) family that has been identified in P. tenuiflora. This gene (1) functionally complemented a yeast mutant deficient in ammonium uptake (2), is preferentially expressed in the anther of P. tenuiflora, and (3) is significantly upregulated by ammonium ions in both the shoot and roots. The PutAMT1;1 protein is localized in the plasma membrane and around the nuclear periphery in yeast cells and P. tenuiflora suspension cells. Immunoelectron microscopy analysis also indicated that PutAMT1;1 is localized in the endomembrane. The overexpression of PutAMT1;1 in A. thaliana enhanced plant growth, and increased plant susceptibility to toxic methylammonium (MeA). Here, we confirmed that PutAMT1;1 is an ammonium-inducible ammonium transporter in P. tenuiflora. On the basis of the results of PutAMT1;1 overexpression in A. thaliana, this gene might be useful for improving the root to shoot mobilization of MeA (or NH4(+)).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
The role of ammonium transporter (AMT) against salt stress in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14(8):1625696. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2019.1625696. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. PMID: 31169446 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the AKT1-type K(+) channel gene from Puccinellia tenuiflora, PutAKT1, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Rep. 2010 Aug;29(8):865-74. doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0872-2. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Plant Cell Rep. 2010. PMID: 20532513
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of plasma membrane- and vacuolar-type Na⁺/H⁺ antiporters of an alkaline-salt-tolerant monocot, Puccinellia tenuiflora.J Plant Res. 2012 Jul;125(4):587-94. doi: 10.1007/s10265-012-0475-9. Epub 2012 Jan 24. J Plant Res. 2012. PMID: 22270695
-
Characterization of AMT-mediated high-affinity ammonium uptake in roots of maize (Zea mays L.).Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Sep;54(9):1515-24. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct099. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23832511
-
Function and Regulation of Ammonium Transporters in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 18;21(10):3557. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103557. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32443561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of AtOxR gene improves abiotic stresses tolerance and vitamin C content in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Biotechnol. 2016 Oct 7;16(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12896-016-0299-0. BMC Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27717369 Free PMC article.
-
Abiotic Stresses Downregulate Key Genes Involved in Nitrogen Uptake and Assimilation in Brassica juncea L.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 25;10(11):e0143645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143645. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26605918 Free PMC article.
-
Host-derived viral transporter protein for nitrogen uptake in infected marine phytoplankton.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 5;114(36):E7489-E7498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708097114. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28827361 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the ammonium transporters gene family in Phaseolus vulgaris and its roles in response to drought and salinity stress.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05795-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594291 Free PMC article.
-
The ctenidium of the giant clam, Tridacna squamosa, expresses an ammonium transporter 1 that displays light-suppressed gene and protein expression and may be involved in ammonia excretion.J Comp Physiol B. 2018 Sep;188(5):765-777. doi: 10.1007/s00360-018-1161-6. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Comp Physiol B. 2018. PMID: 29691634
References
-
- Yuan ZQ (2010) Analysis of Saline-Alkali characteristics and nutrient status of soil in Western Jilin Province. Dissertation, Northeast Normal University, China.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

