Weight control attempts in underweight korean adults: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey, 2007-2010
- PMID: 24340161
- PMCID: PMC3856281
- DOI: 10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.6.393
Weight control attempts in underweight korean adults: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey, 2007-2010
Abstract
Background: Underweight refers to the weight range in which health risk can increase, since the weight is lower than a healthy weight. Negative attitudes towards obesity and socio-cultural preference for thinness could induce even underweight persons to attempt weight control. This study was conducted to investigate factors related to weight control attempts in underweight Korean adults.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study on 690 underweight adults aged 25 to 69 years using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007-2010. Body image perception, weight control attempts during the past one year, various health behaviors, history of chronic diseases, and socioeconomic status were surveyed.
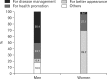
Results: Underweight women had a higher rate of weight control attempts than underweight men (25.4% vs. 8.1%, P < 0.001). Among underweight men, subjects with the highest physical activity level (odds ratio [OR], 7.75), subjects with physician-diagnosed history of chronic diseases (OR, 7.70), and subjects with non-manual jobs or other jobs (OR, 6.22; 12.39 with reference to manual workers) had a higher likelihood of weight control attempts. Among underweight women, subjects who did not perceive themselves as thin (OR, 4.71), subjects with the highest household income level (OR, 2.61), and unmarried subjects (OR, 2.08) had a higher likelihood of weight control attempts.
Conclusion: This study shows that numbers of underweight Korean adults have tried to control weight, especially women. Seeing that there are gender differences in factors related to weight control attempts in underweight adults, gender should be considered in helping underweight adults to maintain a healthy weight.
Keywords: Body Image; Body Weight; Social Class; Underweight; Weight Reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Dwyer J. Policy and healthy weight. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;63(3 Suppl):415S–418S. - PubMed
-
- Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry: report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1995;854:1–452. - PubMed
-
- Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare; Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea health statistics 2010: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1) Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare; 2011.
-
- Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH. Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA. 2007;298:2028–2037. - PubMed
-
- Gelber RP, Kurth T, Manson JE, Buring JE, Gaziano JM. Body mass index and mortality in men: evaluating the shape of the association. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007;31:1240–1247. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

