Sleep and pregnancy-induced hypertension: a possible target for intervention?
- PMID: 24340300
- PMCID: PMC3836349
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.3290
Sleep and pregnancy-induced hypertension: a possible target for intervention?
Abstract
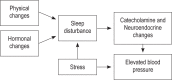
Sleep disturbances in the general population are associated with elevated blood pressure. This may be due to several mechanisms, including sympathetic activation and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis disturbance. Elevated blood pressure in pregnancy can have devastating effects on both maternal and fetal health and is associated with increased risk for preeclampsia and poor delivery outcomes. Preliminary evidence suggests that mechanisms linking sleep and blood pressure in the general population may also hold in the pregnant population. However, the effects of disturbed sleep on physiologic mechanisms that may directly influence blood pressure in pregnancy have not been well studied. The role that sleep disturbance plays in gestational blood pressure elevation and its subsequent consequences warrant further investigation. This review evaluates the current literature on sleep disturbance and elevated blood pressure in pregnancy and proposes possible treatment interventions.
Keywords: Sleep disturbance; blood pressure; hypertension; pregnancy; weight.
Figures
References
-
- Sahota PK, Jain SS, Dhand R. Sleep disorders in pregnancy. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2003;9:477–83. - PubMed
-
- Balserak BI, Lee K. Sleep Disturbances and sleep-related disorders in pregnancy. In: Kryger MH, Roth T, Dement WC, editors. Principles and practice of sleep medicine. 5th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier; 2011. pp. 1572–86.
-
- Kestenbaum B, Seliger SL, Easterling TR, et al. Cardiovascular and thromboembolic events following hypertensive pregnancy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:982–9. - PubMed
-
- Liu CM, Cheng PJ, Chang SD. Maternal complications and perinatal outcomes associated with gestational hypertension and severe preeclampsia in Taiwanese women. J Formos Med Assoc. 2008;107:129–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

