Microarray analysis provides new insights into the function of apolipoprotein O in HepG2 cell line
- PMID: 24341743
- PMCID: PMC3878747
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-186
Microarray analysis provides new insights into the function of apolipoprotein O in HepG2 cell line
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein O (apoO) is a new member of the apolipoprotein family. However, data on its physiological functions are limited and inconsistent. Using a microarray expression analysis, this study explored the function of apoO in liver cells.
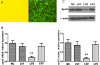
Methods: HepG2 cells were treated either with oleic acid or tumor necrosis factor-α for 24 h. mRNA and protein expression of apoO were assessed by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot respectively. An efficient lentiviral siRNA vector targeting the human apoO gene was designed and constructed. The gene expression profile of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells transfected with the apoO silencing vector was investigated using a whole-genome oligonucleotide microarray. The expression levels of some altered genes were validated using qRT-PCR.
Results: ApoO expression in HepG2 cells was dramatically affected by lipid and inflammatory stimuli. A total of 282 differentially expressed genes in apoO-silenced HepG2 cells were identified by microarray analysis. These genes included those participating in fatty acid metabolism, such as ACSL4, RGS16, CROT and CYP4F11, and genes participating in the inflammatory response, such as NFKBIZ, TNFSF15, USP2, IL-17, CCL23, NOTCH2, APH-1B and N2N. The gene Uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2), which is involved in both these metabolic pathways, demonstrated significant changes in mRNA level after transfection.
Conclusions: It is likely that apoO participates in fatty acid metabolism and the inflammatory response in HepG2 cells, and UCP2 may act as a mediator between lipid metabolism and inflammation in apoO-silenced HepG2 cells.
Figures



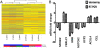
Similar articles
-
Oleic acid induces the novel apolipoprotein O and reduces mitochondrial membrane potential in chicken and human hepatoma cells.Biochimie. 2018 Apr;147:136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 29432786
-
Apolipoprotein O is mitochondrial and promotes lipotoxicity in heart.J Clin Invest. 2014 May;124(5):2277-86. doi: 10.1172/JCI74668. Epub 2014 Apr 17. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24743151 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatosteatosis and estrogen increase apolipoprotein O production in the chicken.Biochimie. 2016 Aug;127:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 27126072
-
Apolipoprotein O expression in mouse liver enhances hepatic lipid accumulation by impairing mitochondrial function.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 9;491(1):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.128. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28647361
-
Uncoupling protein-2 and the potential link between metabolism and longevity.Curr Aging Sci. 2010 Jul;3(2):102-12. doi: 10.2174/1874609811003020102. Curr Aging Sci. 2010. PMID: 20158496 Review.
Cited by
-
PPARδ activation induces hepatic long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4 expression in vivo and in vitro.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1851(5):577-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25645621 Free PMC article.
-
An APOO Pseudogene on Chromosome 5q Is Associated With Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels.Circulation. 2018 Sep 25;138(13):1343-1355. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034016. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29593015 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial apolipoprotein MIC26 is a metabolic rheostat regulating central cellular fuel pathways.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Oct 11;7(12):e202403038. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403038. Print 2024 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39393820 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association analysis of egg production performance in chickens across the whole laying period.BMC Genet. 2019 Aug 14;20(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12863-019-0771-7. BMC Genet. 2019. PMID: 31412760 Free PMC article.
-
Amhr2-Cre-Mediated Global Tspo Knockout.J Endocr Soc. 2020 Jan 12;4(2):bvaa001. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa001. eCollection 2020 Feb 1. J Endocr Soc. 2020. PMID: 32099945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamant M, Smih F, Harmancey R, Philip-Couderc P, Pathak A, Roncalli J, Galinier M, Collet X, Massabuau P, Senard JM. et al.ApoO, a novel apolipoprotein, is an original glycoprotein up-regulated by diabetes in human heart. J Biol Chem. 2006;12(47):36289–36302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510861200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nijstad N, de Boer JF, Lagor WR, Toelle M, Usher D, Annema W, der Giet M, Rader DJ, Tietge UJ. Overexpression of apolipoprotein O does not impact on plasma HDL levels or functionality in human apolipoprotein A-I transgenic mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;12(4):294–299. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.01.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland WL, Brozinick JT, Wang LP, Hawkins ED, Sargent KM, Liu Y, Narra K, Hoehn KL, Knotts TA, Siesky A. et al.Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2007;12(3):167–179. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

