Modulation of p25 and inflammatory pathways by fisetin maintains cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice
- PMID: 24341874
- PMCID: PMC3954948
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12185
Modulation of p25 and inflammatory pathways by fisetin maintains cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice
Abstract
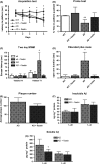
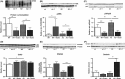
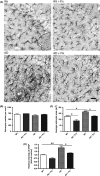
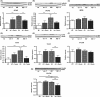
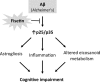
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia. It is the only one of the top ten causes of death in the USA for which prevention strategies have not been developed. Although AD has traditionally been associated with the deposition of amyloid β plaques and tau tangles, it is becoming increasingly clear that it involves disruptions in multiple cellular systems. Therefore, it is unlikely that hitting a single target will result in significant benefits to patients with AD. An alternative approach is to identify molecules that have multiple biological activities that are relevant to the disease. Fisetin is a small, orally active molecule which can act on many of the target pathways implicated in AD. We show here that oral administration of fisetin to APPswe/PS1dE9 double transgenic AD mice from 3 to 12 months of age prevents the development of learning and memory deficits. This correlates with an increase in ERK phosphorylation along with a decrease in protein carbonylation, a marker of oxidative stress. Importantly, fisetin also reduces the levels of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator p35 cleavage product, p25, in both control and AD brains. Elevated levels of p25 relative to p35 cause dysregulation of Cdk5 activity leading to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. These fisetin-dependent changes correlate with additional anti-inflammatory effects, including alterations in global eicosanoid synthesis, and the maintenance of markers of synaptic function in the AD mice. Together, these results suggest that fisetin may provide a new approach to the treatment of AD.
Keywords: ERK; astrogliosis; eicosanoid; lipoxygenase; oxidative stress; prostaglandin.
© 2013 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Beking K, Vieira A. Flavonoid intake and disability-adjuested life years due to Alzheimer’s and related dementias: a population-based study involving twenty-three developed countries. Public Health Nutr. 2010;13:1403–1409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

