Efficacies of ceftazidime-avibactam and ceftazidime against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a murine lung infection model
- PMID: 24342641
- PMCID: PMC3957844
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02161-13
Efficacies of ceftazidime-avibactam and ceftazidime against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a murine lung infection model
Abstract
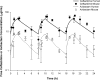
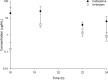
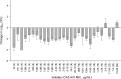
This study aimed to determine the efficacy of human-simulated plasma exposures of 2 g ceftazidime plus 0.5 g avibactam every 8 h administered as a 2-h infusion or a ceftazidime regimen that produced a specific epithelial lining fluid (ELF) percentage of the dosing interval in which serum free drug concentrations remain above the MIC (fT>MIC) against 28 Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates within a neutropenic murine pneumonia model and to assess the impact of host infection on pulmonary pharmacokinetics. The fT>MIC was calculated as the mean and upper end of the 95% confidence limit. Against the 28 P. aeruginosa strains used, the ceftazidime-avibactam MICs were 4 to 64 μg/ml, and those of ceftazidime were 8 to >128 μg/ml. The change in log10 CFU after 24 h of treatment was analyzed relative to that of 0-h controls. Pharmacokinetic studies in serum and ELF were conducted using ceftazidime-avibactam in infected and uninfected mice. Humanized ceftazidime-avibactam doses resulted in significant exposures in the lung, producing reductions of >1 log10 CFU against P. aeruginosa with ceftazidime-avibactam MICs of ≤32 μg/ml (ELF upper 95% confidence limit for fT>MIC [ELF fT>MIC] of ≥19%), except for one isolate with a ceftazidime-avibactam MIC of 16 μg/ml. No efficacy was observed against the isolate with a ceftazidime-avibactam MIC of 64 μg/ml (ELF fT>MIC of 0%). Bacterial reductions were observed with ceftazidime against isolates with ceftazidime MICs of 32 μg/ml (ELF fT>MIC of ≥12%), variable efficacy at ceftazidime MICs of 64 μg/ml (ELF fT>MIC of ≥0%), and no activity at a ceftazidime MIC of 128 μg/ml, where the ELF fT>MIC was 0%. ELF fT>MICs were similar between infected and uninfected mice. Ceftazidime-avibactam was effective against P. aeruginosa, with MICs of up to 32 μg/ml with an ELF fT>MIC of ≥19%. The data suggest the potential utility of ceftazidime-avibactam for treatment of lung infections caused by P. aeruginosa.
Figures


References
-
- Boselli E, Breilh D, Rimmele T, Poupelin JC, Saux MC, Chassard D, Allaouchiche B. 2004. Plasma and lung concentration of ceftazidime administered in continuous infusion to critically ill patients with severe nosocomial pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 30:989–991. 10.1007/s00134-004-2171-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Levasseur P, Girard AM, Claudon M, Goossens H, Black MT, Coleman K, Miossec C. 2012. In vitro antibacterial activity of the ceftazidime-avibactam (NXL104) combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56:1606–1608. 10.1128/AAC.06064-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walkty A, DeCorby M, Lagacé-Wiens PRS, Karlowsky JA, Hoban DJ, Zhanel GG. 2011. In vitro activity of ceftazidime combined with NXL104 versus Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from patients in Canadian hospitals (CANWARD 2009 Study). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55:2992–2994. 10.1128/AAC.01696-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

