The aromatic ene reaction
- PMID: 24345944
- PMCID: PMC4281267
- DOI: 10.1038/nchem.1797
The aromatic ene reaction
Abstract
The ene reaction is a pericyclic process in which an alkene with an allylic hydrogen atom (the ene donor) reacts with a second unsaturated species (the enophile) to form a new product with a transposed π-bond. The aromatic ene reaction, in which the alkene component is embedded in an aromatic ring, has only been reported in a few (four) instances and has proceeded in low yield (≤6%). Here, we show efficient aromatic ene reactions in which a thermally generated aryne intermediate engages a pendant m-alkylarene substituent to produce a dearomatized isotoluene, itself another versatile but rare reactive intermediate. Our experiments were guided by computational studies that revealed structural features conducive to the aromatic ene process. We proceeded to identify a cascade comprising three reactions: (1) hexadehydro-Diels-Alder (for aryne generation), (2) intramolecular aromatic ene and (3) bimolecular Alder ene. The power of this cascade is evident from the structural complexity of the final products, the considerable scope, and the overall efficiency of these multistage, reagent- and by-product-free, single-pot transformations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
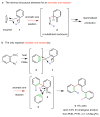

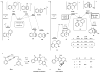

References
-
- Alder K, Pascher F, Schmitz A. Über die Anlagerung von Maleinsäure-anhydrid und Azodicarbonsäure-ester an einfach ungesättigte Koh an einfach ungesättigte Kohlenwasserstoffe. Zur Kenntnis von Substitutionsvorgängen in der Allyl-Stellung. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges. 1943;76:27.
-
- Hoffman HMR. The ene reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1969;8:556–577.
-
- Brinkley YJ, Friedman L. Novel ene and insertion reactions of benzyne and alkylbenzenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1972;13:4141–4142.
-
- Tabushi I, Yamada H, Yoshida Z, Oda R. Reactions of benzyne with substituted benzenes. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1977;50:285–290.
-
- Hoffmann RW. Dehydrobenzene and Cycloalkynes (Organic Chemistry, A Series of Monographs) Vol. 118. Academic; 1967.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/164225752
- PubChem-Substance/164225753
- PubChem-Substance/164225754
- PubChem-Substance/164225755
- PubChem-Substance/164225756
- PubChem-Substance/164225757
- PubChem-Substance/164225758
- PubChem-Substance/164225759
- PubChem-Substance/164225760
- PubChem-Substance/164225761
- PubChem-Substance/164225762
- PubChem-Substance/164225763
- PubChem-Substance/164225764
- PubChem-Substance/164225765
- PubChem-Substance/164225766
- PubChem-Substance/164225767
- PubChem-Substance/164225768
- PubChem-Substance/164225769
- PubChem-Substance/164225770
- PubChem-Substance/164225771
- PubChem-Substance/164225772
- PubChem-Substance/164225773
- PubChem-Substance/164225774
- PubChem-Substance/164225775
- PubChem-Substance/164225776
- PubChem-Substance/164225777
- PubChem-Substance/164225778
- PubChem-Substance/164225779
- PubChem-Substance/164225780
- PubChem-Substance/164225781
- PubChem-Substance/164225782
- PubChem-Substance/164225783
- PubChem-Substance/164225784
- PubChem-Substance/164225785
- PubChem-Substance/164225786
- PubChem-Substance/164225787
- PubChem-Substance/164225788
- PubChem-Substance/164225789
- PubChem-Substance/164225790
- PubChem-Substance/164225791
- PubChem-Substance/164225792
- PubChem-Substance/164225793
- PubChem-Substance/164225794
- PubChem-Substance/164225795
- PubChem-Substance/164225796
- PubChem-Substance/164225797
- PubChem-Substance/164225798
- PubChem-Substance/164225799
- PubChem-Substance/164225800
- PubChem-Substance/164225801
- PubChem-Substance/164225802
- PubChem-Substance/164225803
- PubChem-Substance/164225804
- PubChem-Substance/164225805
- PubChem-Substance/164225806
- PubChem-Substance/164225807
- PubChem-Substance/164225808
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

