Electromagnetic limits to radiofrequency (RF) neuronal telemetry
- PMID: 24346503
- PMCID: PMC3866607
- DOI: 10.1038/srep03535
Electromagnetic limits to radiofrequency (RF) neuronal telemetry
Abstract
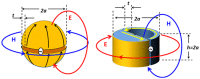
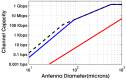
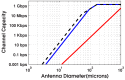
The viability of a radiofrequency (RF) telemetry channel for reporting individual neuron activity wirelessly from an embedded antenna to an external receiver is determined. Comparing the power at the transmitting antenna required for the desired Channel Capacity, to the maximum power that this antenna can dissipate in the body without altering or damaging surrounding tissue reveals the severe penalty incurred by miniaturization of the antenna. Using both Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) and thermal damage limits as constraints, and 300 Kbps as the required capacity for telemetry streams 100 ms in duration, the model shows that conventional antennas smaller than 0.1 mm could not support human neuronal telemetry to a remote receiver (1 m away.) Reducing the antenna to 10 microns in size to enable the monitoring of single human neuron signals to a receiver at the surface of the head would require operating with a channel capacity of only 0.3 bps.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pushing the limits of radiofrequency (RF) neuronal telemetry.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 2;5:10588. doi: 10.1038/srep10588. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26035824 Free PMC article.
-
Wearable wireless telemetry system for implantable bio-MEMS sensors.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;2006:6245-8. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2006.259598. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006. PMID: 17946365
-
Realistic modeling of the biological channel for the design of implantable wireless UWB communication systems.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:6015-8. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347365. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23367300
-
Review on Medical Implantable Antenna Technology and Imminent Research Challenges.Sensors (Basel). 2021 May 2;21(9):3163. doi: 10.3390/s21093163. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAR Simulations & Safety.Neuroimage. 2018 Mar;168:33-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.035. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28336426 Review.
Cited by
-
Implanted cortical neuroprosthetics for speech and movement restoration.J Neurol. 2024 Nov;271(11):7156-7168. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12604-w. Epub 2024 Oct 24. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39446156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bridging the"Last Millimeter" Gap of Brain-Machine Interfaces via Near-Infrared Wireless Power Transfer and Data Communications.ACS Photonics. 2021 May 19;8(5):1430-1438. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00160. Epub 2021 Apr 20. ACS Photonics. 2021. PMID: 34368396 Free PMC article.
-
Pushing the limits of radiofrequency (RF) neuronal telemetry.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 2;5:10588. doi: 10.1038/srep10588. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26035824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mackay R. S. Radio telemetering from within the human body. IRE Trans. Med. Electron. ME-6, 100–105 (1959).
-
- Jensen K., Weldon J., Garcia H. & Zettl A. Nanotube radio. Nano Lett. 7, 3508–3511 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Krishnaswamy D., Ramanathan R. & Qamar A. Collaborative wireless nanobots for tumor discovery and drug delivery. IEEE ICC 2012, Ottawa, 6203–6208 (10.1109/ICC.2012.6364972) (June10–152012).
-
- Cofer G. P., Brown J. M. & Johnson G. A. In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Microscopy at 5 μm. J. Magn. Reson. 83, 608–616 (1989).
-
- Sample P., Waters B. H., Wisdom S. T. & Smith J. R. Enabling Seamless Wireless Power Delivery in Dynamic Environments. Proc. IEEE 101, 1343–1358 (2013).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

