A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury
- PMID: 24346647
- PMCID: PMC3918942
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000052
A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury
Abstract
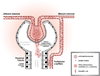
Given that the leading clinical conditions associated with acute kidney injury (AKI), namely, sepsis, major surgery, heart failure, and hypovolemia, are all associated with shock, it is tempting to attribute all AKI to ischemia on the basis of macrohemodynamic changes. However, an increasing body of evidence has suggested that in many patients, AKI can occur in the absence of overt signs of global renal hypoperfusion. Indeed, sepsis-induced AKI can occur in the setting of normal or even increased renal blood flow. Accordingly, renal injury may not be entirely explained solely on the basis of the classic paradigm of hypoperfusion, and thus other mechanisms must come into play. Herein, we put forward a "unifying theory" to explain the interplay between inflammation and oxidative stress, microvascular dysfunction, and the adaptive response of the tubular epithelial cell to the septic insult. We propose that this response is mostly adaptive in origin, that it is driven by mitochondria, and that it ultimately results in and explains the clinical phenotype of sepsis-induced AKI.
Figures


References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005 Aug 17;294(7):813–818. - PubMed
-
- Langenberg C, Wan L, Egi M, May CN, Bellomo R. Renal blood flow in experimental septic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2006 Jun;69(11):1996–2002. - PubMed
-
- Chua HR, Glassford N, Bellomo R. Acute kidney injury after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2012 Jun;83(6):721–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

