Identification of streptococcal m-protein cardiopathogenic epitopes in experimental autoimmune valvulitis
- PMID: 24346820
- PMCID: PMC3943786
- DOI: 10.1007/s12265-013-9526-4
Identification of streptococcal m-protein cardiopathogenic epitopes in experimental autoimmune valvulitis
Abstract
The M protein of rheumatogenic group A streptococci induces carditis and valvulitis in Lewis rats and may play a role in pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease. To identify the epitopes of M5 protein that produce valvulitis, synthetic peptides spanning A, B, and C repeat regions contained within the extracellular domain of the streptococcal M5 protein were investigated. A repeat region peptides NT4, NT5/6, and NT7 induced valvulitis similar to the intact pepsin fragment of M5 protein. T cell lines from rats with valvulitis recognized M5 peptides NT5/6 and NT6. Passive transfer of an NT5/6-specific T cell line into naïve rats produced valvulitis characterized by infiltration of CD4+ cells and upregulation of VCAM-1, while an NT6-specific T cell line did not target the valve. Our new data suggests that M protein-specific T cells may be important mediators of valvulitis in the Lewis rat model of rheumatic carditis.
Figures
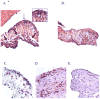

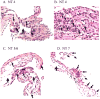
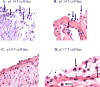
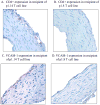

References
-
- Stollerman GH. Rheumatic fever in the 21st century. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33(6):806–14. - PubMed
-
- Stollerman GH. Rheumatic Fever. Lancet. 1997;349:935–942. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham MW. Pathogenesis of Acute Rheumatic Fever. In: Stevens DS, Kaplan EH, editors. Streptococcal Diseases. first. New York, NY: Oxford Press; 2000. pp. 102–132.
-
- Dajani AS. Guidelines for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever (Jones criteria, 1992 update) Journal of the American Medical Association. 1992;268:2069–2073. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

