Crucial positively charged residues for ligand activation of the GPR35 receptor
- PMID: 24347166
- PMCID: PMC3916562
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508382
Crucial positively charged residues for ligand activation of the GPR35 receptor
Abstract
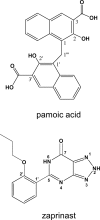
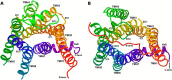
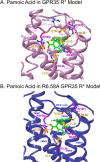
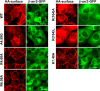
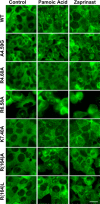
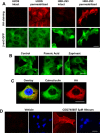
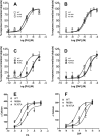
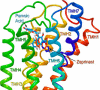
GPR35 is a G protein-coupled receptor expressed in the immune, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems in gastric carcinomas and is implicated in heart failure and pain perception. We investigated residues in GPR35 responsible for ligand activation and the receptor structure in the active state. GPR35 contains numerous positively charged amino acids that face into the binding pocket that cluster in two distinct receptor regions, TMH3-4-5-6 and TMH1-2-7. Computer modeling implicated TMH3-4-5-6 for activation by the GPR35 agonists zaprinast and pamoic acid. Mutation results for the TMH1-2-7 region of GPR35 showed no change in ligand efficacies at the K1.32A, R2.65A, R7.33A, and K7.40A mutants. However, mutation of arginine residues in the TMH3-4-5-6 region (R4.60, R6.58, R3.36, R(164), and R(167) in the EC2 loop) had effects on signaling for one or both agonists tested. R4.60A resulted in a total ablation of agonist-induced activation in both the β-arrestin trafficking and ERK1/2 activation assays. R6.58A increased the potency of zaprinast 30-fold in the pERK assay. The R(167)A mutant decreased the potency of pamoic acid in the β-arrestin trafficking assay. The R(164)A and R(164)L mutants decreased potencies of both agonists. Similar trends for R6.58A and R(167)A were observed in calcium responses. Computer modeling showed that the R6.58A mutant has additional interactions with zaprinast. R3.36A did not express on the cell surface but was trapped in the cytoplasm. The lack of surface expression of R3.36A was rescued by a GPR35 antagonist, CID2745687. These results clearly show that R4.60, R(164), R(167), and R6.58 play crucial roles in the agonist initiated activation of GPR35.
Keywords: Arrestin; G Protein-coupled Receptors (GPCR); MAP Kinases (MAPKs); Molecular Modeling; Trafficking.
Figures


References
-
- O'Dowd B. F., Nguyen T., Marchese A., Cheng R., Lynch K. R., Heng H. H., Kolakowski L. F., Jr., George S. R. (1998) Discovery of three novel G-protein-coupled receptor genes. Genomics 47, 310–313 - PubMed
-
- Guo J., Williams D. J., Puhl H. L., 3rd, Ikeda S. R. (2008) Inhibition of N-type calcium channels by activation of GPR35, an orphan receptor, heterologously expressed in rat sympathetic neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 324, 342–351 - PubMed
-
- Ohshiro H., Tonai-Kachi H., Ichikawa K. (2008) GPR35 is a functional receptor in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 365, 344–348 - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi Y., Tonai-Kachi H., Shinjo K. (2006) Zaprinast, a well-known cyclic guanosine monophosphate-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor, is an agonist for GPR35. FEBS Lett. 580, 5003–5008 - PubMed
-
- Zhao P., Sharir H., Kapur A., Cowan A., Geller E. B., Adler M. W., Seltzman H. H., Reggio P. H., Heynen-Genel S., Sauer M., Chung T. D., Bai Y., Chen W., Caron M. G., Barak L. S., Abood M. E. (2010) Targeting of the orphan receptor GPR35 by pamoic acid. A potent activator of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and β-arrestin2 with antinociceptive activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 78, 560–568 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

