Effect of melatonin and gabapentin on anxiety and pain associated with retrobulbar eye block for cataract surgery: a randomized double-blind study
- PMID: 24347765
- PMCID: PMC3847247
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.121368
Effect of melatonin and gabapentin on anxiety and pain associated with retrobulbar eye block for cataract surgery: a randomized double-blind study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the effect of melatonin and gabapentin on anxiety, pain, sedation scores, and satisfaction of surgeon in patients of cataract surgery.
Materials and methods: One hundred thirty patients aged between 35 and 85 years scheduled for cataract surgery were randomly allocated to three study groups to receive melatonin (6 mg), gabapentin (600 mg) or placebo 90 min before arrival in the operating room. Pain, anxiety, and sedation scores during block and surgery as well as the surgeon's satisfaction with the surgery were assessed.
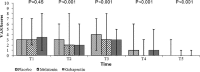
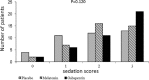
Results: Anxiety scores decreased significantly in melatonin and gabapentin groups compared to the placebo group after premedication and extended to early postoperative period. The level of anxiety showed no statistically significant difference between melatonin and gabapentin groups at any time of measurement. There were significant differences between the pain scores during retrobulbar placement in gabapentin versus placebo (95% CI 3 to 4; P = 0.001) and melatonin (95% CI 3 to 4; P = 0.040) groups. Also, there were significant differences between the sedation scores during retrobulbar placement in gabapentin and placebo groups (95% CI 2 to 2.5; P = 0.046). The difference in sedation scores during retrobulbar placement in melatonin versus gabapentin and placebo groups was not significant. Neither the intraoperative pain scores nor the postoperative pain scores were different between the three groups. The surgeon reported similar quality of operation conditions during surgery for the three study groups.
Conclusion: The level of anxiety was significantly lower with both anxiolytic drugs compared to placebo. Furthermore, gabapentin decreased the pain and improved the sedation scores only during retrobulbar placement compared to the placebo.
Keywords: Anxiety; cataract; gabapentin; melatonin; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Alhashemi JA. Dexmedetomidinevs midazolamfor monitored anaesthesiacare during cataract surgery. BrJ Anaesth. 2006;96:722–6. - PubMed
-
- Yousaf F, Seet E, Venkatraghavan L, Abrishami A, Chung F. Efficacy and safety of melatonin as an anxiolytic and analgesic in the perioperative period. Anesthesiology. 2010;113:968–76. - PubMed
-
- Kong VK, Irwin MG. Gabapentin: A multimodal perioperative drug? Br J Anaesth. 2007;99:775–86. - PubMed
-
- Otmani S, Demazie` A, Staner C, Jacob N, Nir T, Zisapel N, et al. Effects of prolonged-release melatonin, zolpidem, and their combination on psychomotor functions, memory recall, and driving skills in healthy middle aged and elderly volunteers. HumPsychopharmacol. 2008;23:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Naguib M, Gottumukkala V, Goldstein P. Melatonin and anesthesia: A clinical perspective. JPineal Res. 2007;42:12–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

