Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase mediates diabetes-induced retinal neuropathy
- PMID: 24347828
- PMCID: PMC3857786
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/510451
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase mediates diabetes-induced retinal neuropathy
Abstract
Retinal neuropathy is an early event in the development of diabetic retinopathy. One of the potential enzymes that are activated by oxidative stress in the diabetic retina is poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). We investigated the effect of the PARP inhibitor 1,5-isoquinolinediol on the expression of the neurodegeneration mediators and markers in the retinas of diabetic rats. After two weeks of streptozotocin-induced diabetes, rats were treated with 1,5-isoquinolinediol (3 mg/kg/day). After 4 weeks of diabetes, the retinas were harvested and the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were determined fluorometrically and the expressions of PARP, phosporylated-ERK1/2, BDNF, synaptophysin, glutamine synthetase (GS), and caspase-3 were determined by Western blot analysis. Retinal levels of ROS, PARP-1/2, phosphorylated ERK1/2, and cleaved caspase-3 were significantly increased, whereas the expressions of BDNF synaptophysin and GS were significantly decreased in the retinas of diabetic rats, compared to nondiabetic rats. Administration of 1,5-isoquinolinediol did not affect the metabolic status of the diabetic rats, but it significantly attenuated diabetes-induced upregulation of PARP, ROS, ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and cleaved caspase-3 and downregulation of BDNF, synaptophysin, and GS. These findings suggest a beneficial effect of the PARP inhibitor in increasing neurotrophic support and ameliorating early retinal neuropathy induced by diabetes.
Figures


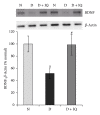


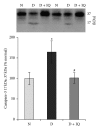
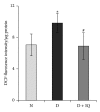
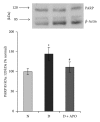
References
-
- Seki M, Tanaka T, Nawa H, et al. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in early retinal neuropathy of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic amacrine cells. Diabetes. 2004;53(9):2412–2419. - PubMed
-
- Barber AJ. A new view of diabetic retinopathy: a neurodegenerative disease of the eye. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2003;27(2):283–290. - PubMed
-
- Simó R, Hernández C, European consortium for the early treatment of diabetic retinopathy (EUROCONDOR) Neurodegeneration is an early event in diabetic retinopathy: therapeutic implications. British Journal of Ophthalmology. 2012;96(10):1285–1290. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

