P-glycoprotein alters blood-brain barrier penetration of antiepileptic drugs in rats with medically intractable epilepsy
- PMID: 24348021
- PMCID: PMC3857069
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S52533
P-glycoprotein alters blood-brain barrier penetration of antiepileptic drugs in rats with medically intractable epilepsy
Abstract
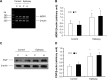
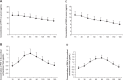
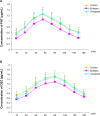
P-glycoprotein is one of the earliest known multidrug transporters and plays an important role in resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. In this study, we detected levels of P-glycoprotein and its mRNA expression in a rat brain model of medically intractable epilepsy established by amygdala kindling and drug selection. We investigated whether inhibition of P-glycoprotein affects the concentration of antiepileptic drugs in cortical extracellular fluid. We found that levels of P-glycoprotein and its mRNA expression were upregulated in epileptic cerebral tissue compared with cerebral tissue from normal rats. The concentrations of two antiepileptic drugs, carbamazepine and phenytoin, were very low in the cortical extracellular fluid of rats with medically intractable epilepsy, and were restored after blockade of P-glycoprotein by verapamil. These results show that increased P-glycoprotein levels alter the ability of carbamazepine and phenytoin to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and reduce the concentrations of these agents in extracellular cortical fluid. High P-glycoprotein levels may be involved in resistance to antiepileptic drugs in medically intractable epilepsy.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein; amygdala kindling; antiepileptic drugs; medically intractable epilepsy; verapamil.
Figures
References
-
- Elia M, Amato C, Bottitta M, et al. An atypical patient with Cowden syndrome and PTEN gene mutation presenting with cortical malformation and focal epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2012;34(10):873–876. - PubMed
-
- Elia M, Falco M, Ferri R, et al. CDKL5 mutations in boys with severe encephalopathy and early-onset intractable epilepsy. Neurology. 2008;2371(13):997–999. - PubMed
-
- Capovilla G, Beccaria F, Montagnini A, et al. Short-term nonhormonal and nonsteroid treatment in West syndrome. Epilepsia. 2003;44(8):1085–1088. - PubMed
-
- Loscher W, Potschka H. Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;76(1):22–76. - PubMed
-
- Potschka H, Loscher W. Multidrug resistance-associated protein is involved in the regulation of extracellular levels of phenytoin in the brain. Neuroreport. 2001;12(11):2387–2389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

