Synchronous BRAF(V600E) and MEK inhibition leads to superior control of murine melanoma by limiting MEK inhibitor induced skin toxicity
- PMID: 24348046
- PMCID: PMC3849083
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S52552
Synchronous BRAF(V600E) and MEK inhibition leads to superior control of murine melanoma by limiting MEK inhibitor induced skin toxicity
Abstract
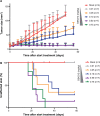
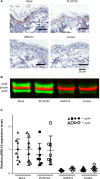
The BRAF inhibitor (BRAFi) treatment has led to impressive responses in BRAF(V600E) mutation-positive melanomas, but responses are not durable in many patients. As most of the BRAFi escape mechanisms involve ERK reactivation, combinations with MEK inhibitors (MEKi) are currently tested to improve BRAFi-mediated response durations. Additionally, such a combination is expected to reduce MEKi-induced skin toxicities, as these drugs are thought to have antagonistic effects on ERK activation in keratinocytes. However, preclinical in vivo data exploring the combination of BRAFi and MEKi to achieve improved tumor control in the absence of skin toxicities are limited. Using a murine Tyr::CreER(T2);Pten(LoxP/LoxP);Braf(CA/+) melanoma model, we have determined the effect of BRAFi and MEKi treatment and their combination on melanoma control and occurrence of adverse events. We found that the MEKi dosed beyond the maximum tolerable dose (MTD) led to stronger control of tumor growth than did the BRAFi, but mice had to be removed from treatment because of skin toxicity. The combination of BRAFi and MEKi reduced MEKi-associated skin toxicity. This allowed high and long-term dosing of the MEKi, resulting in long-term tumor control. In contrast to previous hypotheses, the addition of a BRAFi did not restore the MEKi-mediated downregulation of pERK1/2 in skin cells. Our data describe, for the first time, the alleviation of MEKi-mediated dose-limiting toxicity by addition of a BRAFi in a mouse melanoma model. Additional clinical Phase I studies should be implemented to explore MEKi dosing beyond the single drug MTD in combination with BRAFi.
Keywords: BRAF; MEK; melanoma; skin toxicity; trametinib; vemurafenib.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory effects of BRAF and MEK inhibitors: Implications for Melanoma therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Oct;136:151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30145328 Review.
-
ER Translocation of the MAPK Pathway Drives Therapy Resistance in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma.Cancer Discov. 2019 Mar;9(3):396-415. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0348. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30563872 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of BRAF Inhibitors With or Without MEK Inhibitors in BRAF-Mutant Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Findings From a Real-Life Cohort.Clin Lung Cancer. 2019 Jul;20(4):278-286.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31060855
-
Adverse effects of systemic advanced melanoma therapies-do BRAF/MEK inhibitors increase the incidence of mesenteric panniculitis?Eur Radiol. 2025 May 1. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11642-w. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40310541
-
Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of cardiac toxicity induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors and BRAF and MEK inhibitors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Nov;100:102282. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102282. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34438238 Review.
Cited by
-
The Tubulin Inhibitor VERU-111 in Combination With Vemurafenib Provides an Effective Treatment of Vemurafenib-Resistant A375 Melanoma.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;12:637098. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.637098. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33841154 Free PMC article.
-
RAF dimer inhibition enhances the antitumor activity of MEK inhibitors in K-RAS mutant tumors.Mol Oncol. 2020 Aug;14(8):1833-1849. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12698. Epub 2020 May 18. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32336014 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the MAPK and PI3K pathways in combination with PD1 blockade in melanoma.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Oct 14;5(12):e1238557. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1238557. eCollection 2016. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 28123875 Free PMC article.
-
A potent tumor-selective ERK pathway inactivator with high therapeutic index.PNAS Nexus. 2022 Jul 1;1(3):pgac104. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgac104. eCollection 2022 Jul. PNAS Nexus. 2022. PMID: 35899070 Free PMC article.
-
BRAF Inhibitors for the Treatment of Papulopustular Eruptions from MAPK Pathway Inhibitors.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020 Dec;21(6):759-764. doi: 10.1007/s40257-020-00539-7. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32720072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smalley KS. Understanding melanoma signaling networks as the basis for molecular targeted therapy. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130(1):28–37. - PubMed
-
- Hauschild A, Grob J, Demidov L, et al. Phase III, randomized, open-label, multicenter trial (BREAK-3) comparing the BRAF kinase inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436) with dacarbazine (DTIC) in patients with BRAFV600E-mutated melanoma; Annual Meeting Program, American Society of Clinical Oncology; June 1–5, 2012; Chicago, IL, USA. Abstract LBA 8500.
-
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al. METRIC Study Group Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(2):107–114. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

