System for simultaneous measurements of bilaterally symmetrical acupoints multifrequency impedances
- PMID: 24348077
- PMCID: PMC3850687
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S52903
System for simultaneous measurements of bilaterally symmetrical acupoints multifrequency impedances
Abstract
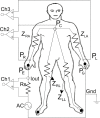
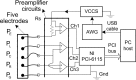
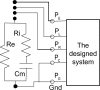
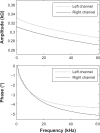
Devices which can obtain comparable bilaterally symmetrical acupoints (BSA) multifrequency impedances (MFI) are often needed in the detection of the energy balance states of acupoints in traditional Chinese medicine. To satisfy these needs, a two-channel impedance measurement system has been introduced which is capable of accurately and simultaneously measuring BSA MFI. The system includes a set of five electrodes, two of which are injected with exciting current signal to synchronously and equally excite BSA; the other three electrodes are used as sensors to simultaneously sense the response signal from both sides. The system also includes a PC-based time-domain signal testing platform with arbitrary current waveform generation and three channels (one exciting current and two response voltages) simultaneously sampling, and a set of MFI simultaneously unbiased computing algorithms based on special odd multisine current signal input. Preliminary validating experiments suggest that the system allows accurate and synchronous measurement of BSA MFI at least in the frequency range of 10 Hz to 60 kHz, and the obtained BSA MFI are well comparable.
Keywords: Qi; acupuncture; balance; meridians; two-channel.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A birdcage model for the Chinese Meridian System: part I. A channel as a transmission line.Am J Chin Med. 2004;32(5):815-28. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X04002417. Am J Chin Med. 2004. PMID: 15633816
-
Mechanism of acupuncture regulating visceral sensation and mobility.Front Med. 2011 Jun;5(2):151-6. doi: 10.1007/s11684-011-0129-7. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Front Med. 2011. PMID: 21695619 Review.
-
Development and evaluation of a novel four-electrode device system for monitoring skin impedance.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012 Jul 1;9(4):599-606. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v9i4.18. eCollection 2012. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 23983397 Free PMC article.
-
A new bioimpedance research device (BIRD) for measuring the electrical impedance of acupuncture meridians.J Altern Complement Med. 2010 Mar;16(3):257-64. doi: 10.1089/acm.2009.0218. J Altern Complement Med. 2010. PMID: 20192910
-
Birdcage model for the Chinese meridian system: part VI. meridians as the primary regulatory system.Am J Chin Med. 2005;33(5):759-66. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X05003302. Am J Chin Med. 2005. PMID: 16265988 Review.
References
-
- Navarra Tova. The Encyclopedia of Complementary and Alternative Medicine. New York: Facts on File; 2004.
-
- Lu WA, Tsuei JJ, Chen KG. Preferential direction and symmetry of electric conduction of human meridians: Bilaterally symmetrical acupoints provide better conductance for a better “connection”. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1999;18(1):76–78. - PubMed
-
- Zhou YP, Wang KM, Hu L, et al. Meridian-viscera correlationship. In: Ying X, Ding GH, Wu GC, editors. Current Research in Acupuncture. New York: Springer; 2013. pp. 559–599.
-
- Halter RJ, Hartov A, Heaney JA, Paulsen KD, Schned AR. Electrical impedance spectroscopy of the human prostate. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2007;54(7):1321–1327. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

