Insights on the phytochemical profile (cyclopeptides) and biological activities of Calotropis procera latex organic fractions
- PMID: 24348174
- PMCID: PMC3852081
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/615454
Insights on the phytochemical profile (cyclopeptides) and biological activities of Calotropis procera latex organic fractions
Abstract
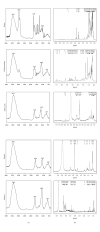
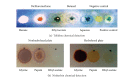
Calotropis procera is a medicinal plant whose pharmacological properties are associated with its latex. Here, the Calotropis procera latex fractions were investigated in an attempt to trace its phytochemical profile and measure its anti-inflammatory and toxicity activity. The crude latex was partitioned, yielding five fractions (49.4% hexane, 5.2% dichloromethane, 2.0% ethyl acetate, 2.1% n-butanol, and 41.1% aqueous). Phytochemical screening and spectroscopy analysis revealed that dichloromethane is the most chemically diverse fraction. Triterpenes were detected in both the hexane and dichloromethane fractions, while flavonoids were detected in the dichloromethane and ethyl acetate fractions. These fractions were cytotoxic to cancer cell lines (LD50 0.05 to 3.9 μ g/mL) and lethal to brine shrimp (LD50 10.9 to 65.7 μ g/mL). Reduced neutrophil migration in rats was observed in carrageenan-induced peritonitis for the dichloromethane (67%), ethyl acetate (56%), and aqueous (72%) fractions. A positive reaction with tolidine and ninhydrin suggested that cyclopeptides are in the ethyl acetate fraction. It is therefore concluded that Calotropis procera latex dichloromethane and ethyl acetate fractions exhibit both in vitro and in vivo activities as well as anti-inflammatory properties. Cyclopeptide detection is especially interesting because previous attempts to investigate these low-molecular cyclic amino acid sequences in C. procera have failed.
Figures
References
-
- Chundattu SJ, Agrawal VK, Ganesh N. Phytochemical investigation of Calotropis procera . Arabian Journal of Chemistry. 2011
-
- Kumar VL, Arya S. Medicinal uses and pharmacological properties of Calotropis procera . In: Govil JN, editor. Recent Progress in Medicinal Planta. Vol. 11. Texas Studium Press; 2006. pp. 373–388.
-
- Oh SK, Kang H, Shin DH, Yang J, Han KH. Molecular cloning and characterization of a functional cDNA clone encoding isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase from Hevea brasiliensis. Journal of Plant Physiology. 2000;157(5):549–557.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials