Investigations of homologous recombination pathways and their regulation
- PMID: 24348209
- PMCID: PMC3848099
Investigations of homologous recombination pathways and their regulation
Abstract
The DNA double-strand break (DSB), arising from exposure to ionizing radiation or various chemotherapeutic agents or from replication fork collapse, is among the most dangerous of chromosomal lesions. DSBs are highly cytotoxic and can lead to translocations, deletions, duplications, or mutations if mishandled. DSBs are eliminated by either homologous recombination (HR), which uses a homologous template to guide accurate repair, or by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), which simply rejoins the two broken ends after damaged nucleotides have been removed. HR generates error-free repair products and is also required for generating chromosome arm crossovers between homologous chromosomes in meiotic cells. The HR reaction includes several distinct steps: resection of DNA ends, homologous DNA pairing, DNA synthesis, and processing of HR intermediates. Each occurs in a highly regulated fashion utilizing multiple protein factors. These steps are being elucidated using a combination of genetic tools, cell-based assays, and in vitro reconstitution with highly purified HR proteins. In this review, we summarize contributions from our laboratory at Yale University in understanding HR mechanisms in eukaryotic cells.
Keywords: DNA repair; double Holliday junction; double-strand breaks; homologous recombination; presynaptic filament; recombinase; resection; synaptic complex.
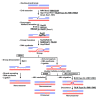
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex in double-strand break repair-facts and myths.J Radiat Res. 2016 Aug;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i25-i32. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw034. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27311583 Free PMC article.
-
Release of Ku and MRN from DNA ends by Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 is required for homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002271. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21931565 Free PMC article.
-
Rad51 recruitment and exclusion of non-homologous end joining during homologous recombination at a Tus/Ter mammalian replication fork barrier.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 19;14(7):e1007486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007486. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30024881 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of homologous recombination in response to ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(6):903-914. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2021.1956001. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 34283012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathways and assays for DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019 Sep 6;51(9):879-889. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmz076. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019. PMID: 31294447 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of OB-Fold Proteins in Replication Stress.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 11;8:574466. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.574466. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33043007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational environmental switch of RadA activity by extein-intein interactions in protein splicing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 27;43(13):6631-48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv612. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26101259 Free PMC article.
-
Amentoflavone triggers cell cycle G2/M arrest by interfering with microtubule dynamics and inducing DNA damage in SKOV3 cells.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):168. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12031. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32934735 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of Rad51c predicts poor prognostic outcome and induces cell resistance to cisplatin and radiation in non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13489-13498. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5192-x. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27465554
-
Nrf2 promotes survival following exposure to ionizing radiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.035. Epub 2015 May 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25975985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trujillo KM, Roh DH, Chen L, Van Komen S, Tomkinson A, Sung P. Yeast xrs2 binds DNA and helps target rad50 and mre11 to DNA ends. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(49):48957–48964. - PubMed
-
- Trujillo KM, Sung P. DNA structure-specific nuclease activities in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad50*Mre11 complex. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(38):35458–35464. - PubMed
-
- Trujillo KM, Yuan SS, Lee EY, Sung P. Nuclease activities in a complex of human recombination and DNA repair factors Rad50, Mre11, and p95. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(34):21447–21450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
