GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors and AMPA receptors in medial prefrontal cortex are necessary for odor span in rats
- PMID: 24348356
- PMCID: PMC3845012
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00183
GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors and AMPA receptors in medial prefrontal cortex are necessary for odor span in rats
Abstract
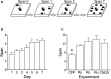
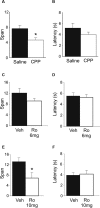
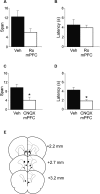
Working memory is a type of short-term memory involved in the maintenance and manipulation of information essential for complex cognition. While memory span capacity has been extensively studied in humans as a measure of working memory, it has received considerably less attention in rodents. Our aim was to examine the role of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) glutamate receptors in odor span capacity using systemic injections or infusions of receptor antagonists into the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Long Evans rats were trained on a well-characterized odor span task (OST). Initially, rats were trained to dig for a food reward in sand followed by training on a non-match to sample discrimination using sand scented with household spices. The rats were then required to perform a serial delayed non-match to sample procedure which was their odor span. Systemic injection of the broad spectrum NMDA receptor antagonist 3-(2-Carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP) (10 mg/kg) or the GluN2B-selective antagonist Ro 25-6981 (10 mg/kg but not 6 mg/kg) significantly reduced odor span capacity. Infusions of the GluN2B- selective antagonist Ro 25-6981 (2.5 μg/hemisphere) into mPFC reduced span capacity, an effect that was nearly significant (p = 0.069). Infusions of the AMPA receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) (1.25 μg/hemisphere) into mPFC reduced span capacity and latency for the rats to make a choice in the task. These results demonstrate span capacity in rats depends on ionotropic glutamate receptor activation in the mPFC. Further understanding of the circuitry underlying span capacity may aid in the novel therapeutic drug development for persons with working memory impairments as a result of disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: CNQX; CPP; Ro 25-6981; glutamate; odor span task; working memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interactions between medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum are necessary for odor span capacity in rats: role of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors.Learn Mem. 2017 Sep 15;24(10):524-531. doi: 10.1101/lm.045419.117. Print 2017 Oct. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28916627 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of pharmacological manipulations of NMDA and cholinergic receptors on working versus reference memory in a dual component odor span task.Learn Mem. 2016 May 18;23(6):270-7. doi: 10.1101/lm.041251.115. Print 2016 Jun. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27194794 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal cortical GABAergic and NMDA glutamatergic regulation of delayed responding.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Feb;113(Pt A):10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.09.022. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27678413
-
Contribution of AMPA and NMDA receptors to excitatory responses in the inferior colliculus.Hear Res. 2002 Jun;168(1-2):35-42. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(02)00372-6. Hear Res. 2002. PMID: 12117507 Review.
-
[Role of excitatory amino acids in neuropathology].Medicina (B Aires). 1995;55(4):355-65. Medicina (B Aires). 1995. PMID: 8728878 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Interactions between medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum are necessary for odor span capacity in rats: role of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors.Learn Mem. 2017 Sep 15;24(10):524-531. doi: 10.1101/lm.045419.117. Print 2017 Oct. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28916627 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral pharmacology of the odor span task: Effects of flunitrazepam, ketamine, methamphetamine and methylphenidate.J Exp Anal Behav. 2016 Nov;106(3):173-194. doi: 10.1002/jeab.224. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Exp Anal Behav. 2016. PMID: 27747877 Free PMC article.
-
Medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum are necessary for the trial-unique, delayed nonmatching-to-location (TUNL) task in rats: role of NMDA receptors.Learn Mem. 2017 May 15;24(6):262-266. doi: 10.1101/lm.044750.116. Print 2017 Jun. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28507036 Free PMC article.
-
Amnestic drugs in the odor span task: Effects of flunitrazepam, zolpidem and scopolamine.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Nov;145:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28893667 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of pharmacological manipulations of NMDA and cholinergic receptors on working versus reference memory in a dual component odor span task.Learn Mem. 2016 May 18;23(6):270-7. doi: 10.1101/lm.041251.115. Print 2016 Jun. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27194794 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

