Forme Fruste Keratoconus Imaging and Validation via Novel Multi-Spot Reflection Topography
- PMID: 24348403
- PMCID: PMC3843937
- DOI: 10.1159/000356123
Forme Fruste Keratoconus Imaging and Validation via Novel Multi-Spot Reflection Topography
Abstract
Background/aims: This case report aims to evaluate safety, efficacy and applicability of anterior surface imaging in a patient with forme fruste keratoconus (FFKC) based on a novel multi-spot, multicolor light-emitting-diode (LED) tear film-reflection imaging technology.
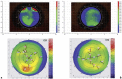
Case description: A 45-year-old male patient, clinically diagnosed with FFKC, with highly asymmetric manifestation between his eyes, was subjected to the multicolor-spot reflection topography. We investigated elevation and sagittal curvature maps comparatively with the multicolor-spot reflection topographer, a Placido topographer and a Scheimpflug imaging system. For the right eye, steep and flat keratometry values were 41.92 and 41.05 D with the multicolor spot-reflection topographer, 42.30 and 42.08 D with the Placido, and 41.95 and 41.19 D with the Scheimpflug system. For the left eye, steep and flat keratometry values were 41.86 and 41.19 D with the multicolor spot-reflection topographer, 42.06 and 41.66 D with the Placido topographer, and 41.96 and 41.66 D with the Scheimpflug camera. Average repeatability of the keratometry measurements was ±0.35 D for the multicolor spot-reflection topographer, ±0.30 D for the Placido, and ±0.25 D for the Scheimpflug camera. Very good agreement between the instruments was demonstrated on the elevation and curvature maps.
Conclusion: The ease of use and the comparable results offered by the multicolor spot-reflection topographer, in comparison to established Placido and Scheimpflug imaging, as well as the increased predictability that may be offered by the multicolor spot-reflection topographer, may hold promise for wider clinical application, such as screening of young adults for early keratoconus and, in a much wider perspective, potential candidates for laser corneal refractive surgery.
Keywords: Color-point topography; Diagnosis of keratoconus; Differential topography; Forme fruste keratoconus; Index of Height Decentration; Index of Surface Variance; Light-emitting diode Cassini; Light-emitting diode topography; Pentacam HR; Placido topography; Point-source topography; Surface Asymmetry Index; Surface Regularity Index.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical Correlation between Placido, Scheimpflug and LED Color Reflection Topographies in Imaging of a Scarred Cornea.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2014 Oct 1;5(3):311-7. doi: 10.1159/000365962. eCollection 2014 Sep. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25408671 Free PMC article.
-
Color light-emitting diode reflection topography: validation of keratometric repeatability in a large sample of wide cylindrical-range corneas.Clin Ophthalmol. 2015 Feb 5;9:245-52. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S68371. eCollection 2015. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25709385 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of three-dimensional optical coherence tomography and combining a rotating Scheimpflug camera with a Placido topography system for forme fruste keratoconus diagnosis.Br J Ophthalmol. 2013 Dec;97(12):1554-9. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-303477. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24081501 Clinical Trial.
-
Galilei Corneal Tomography for Screening of Refractive Surgery Candidates: A Review of the Literature, Part II.Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. 2019 Fall;8(3):204-218. Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31598521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for improving the early diagnosis of keratoconus.Clin Optom (Auckl). 2016 Feb 24;8:13-21. doi: 10.2147/OPTO.S63486. eCollection 2016. Clin Optom (Auckl). 2016. PMID: 30214345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Correlation between Placido, Scheimpflug and LED Color Reflection Topographies in Imaging of a Scarred Cornea.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2014 Oct 1;5(3):311-7. doi: 10.1159/000365962. eCollection 2014 Sep. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25408671 Free PMC article.
-
Color light-emitting diode reflection topography: validation of keratometric repeatability in a large sample of wide cylindrical-range corneas.Clin Ophthalmol. 2015 Feb 5;9:245-52. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S68371. eCollection 2015. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25709385 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors for Development of Keratoconus: A Matched Pair Case-Control Study.Clin Ophthalmol. 2021 Aug 16;15:3473-3479. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S248724. eCollection 2021. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34429579 Free PMC article.
-
Current Developments in Corneal Topography and Tomography.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Aug 13;11(8):1466. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081466. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparability and repeatability of different methods of corneal astigmatism assessment.Clin Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec 20;12:29-34. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S146730. eCollection 2018. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29339918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vos FM, van der Heijde RGL, Spoelder HJW, van Stokkum IHM, Groen FCA. A new instrument to measure the shape of the cornea based on pseudorandom color coding. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 1997;46:794–797.
-
- Snellenburg JJ, Braaf B, Hermans EA, van der Heijde RG, Sicam VA. Forward ray tracing for image projection prediction and surface reconstruction in the evaluation of corneal topography systems. Opt Express. 2010;18:19324–19338. - PubMed
-
- Rand RH, Howland HC, Applegate RA. Mathematical model of a Placido disk keratometer and its implications for recovery of corneal topography. Optom Vis Sci. 1997;74:926–930. - PubMed
-
- Sicam VA, Snellenburg JJ, van der Heijde RG, van Stokkum IH. Pseudo forward ray-tracing: a new method for surface validation in cornea topography. Optom Vis Sci. 2007;84:915–923. - PubMed
-
- Sicam VA, van der Heijde RG. Topographer reconstruction of the nonrotation-symmetric anterior corneal surface features. Optom Vis Sci. 2006;83:910–918. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

