Curcumin and diabetes: a systematic review
- PMID: 24348712
- PMCID: PMC3857752
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/636053
Curcumin and diabetes: a systematic review
Abstract
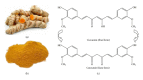
Turmeric (Curcuma longa), a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant of the ginger family, has been used for the treatment of diabetes in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine. The active component of turmeric, curcumin, has caught attention as a potential treatment for diabetes and its complications primarily because it is a relatively safe and inexpensive drug that reduces glycemia and hyperlipidemia in rodent models of diabetes. Here, we review the recent literature on the applications of curcumin for glycemia and diabetes-related liver disorders, adipocyte dysfunction, neuropathy, nephropathy, vascular diseases, pancreatic disorders, and other complications, and we also discuss its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The applications of additional curcuminoid compounds for diabetes prevention and treatment are also included in this paper. Finally, we mention the approaches that are currently being sought to generate a "super curcumin" through improvement of the bioavailability to bring this promising natural product to the forefront of diabetes therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antidotal or protective effects of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and its active ingredient, curcumin, against natural and chemical toxicities: A review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Mar;99:411-421. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.072. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29367110 Review.
-
Curcumin, the active substance of turmeric: its effects on health and ways to improve its bioavailability.J Sci Food Agric. 2021 Nov;101(14):5747-5762. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11372. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Sci Food Agric. 2021. PMID: 34143894 Review.
-
Turmeric and Curcumin: From Traditional to Modern Medicine.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1291:15-39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-56153-6_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34331682
-
The protective effects of curcumin against cigarette smoke-induced toxicity: A comprehensive review.Phytother Res. 2024 Jan;38(1):98-116. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8035. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 37813398 Review.
-
An update on molecular mechanisms of curcumin effect on diabetes.J Food Biochem. 2022 Oct;46(10):e14358. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14358. Epub 2022 Aug 9. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35945662 Review.
Cited by
-
The Maximum-Tolerated Dose and Pharmacokinetics of a Novel Chemically Modified Curcumin in Rats.J Exp Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 9;14:73-85. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S341927. eCollection 2022. J Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35173493 Free PMC article.
-
An Investigation for Skin Tissue Regeneration Enhancement/Augmentation by Curcumin-Loaded Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SEDDS).Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 17;14(14):2904. doi: 10.3390/polym14142904. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890680 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of curcumin in a rat model of postoperative pain.Sci Rep. 2014 May 12;4:4932. doi: 10.1038/srep04932. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24816565 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes and Its Cardiovascular Complications: Potential Role of the Acetyltransferase p300.Cells. 2023 Jan 28;12(3):431. doi: 10.3390/cells12030431. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of diabetes on male sexual function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Protective role of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jul;115:108897. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108897. Epub 2019 May 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31102913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shapiro K, Gong WC. Natural products used for diabetes. Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association. 2002;42(2):217–226. - PubMed
-
- Gobert CP, Duncan AM. Consumption, perceptions and knowledge of soy among adults with type 2 diabetes. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2009;28(2):203–218. - PubMed
-
- Nolan CJ, Damm P, Prentki M. Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management. The Lancet. 2011;378(9786):169–181. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N, Ichikawa H. Curcumin: the Indian solid gold. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2007;595:1–75. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

